Figure 6.
Light-Induced PIF3 Phosphorylation and Degradation Are Necessary for Negative Feedback Modulation of phyB Levels.
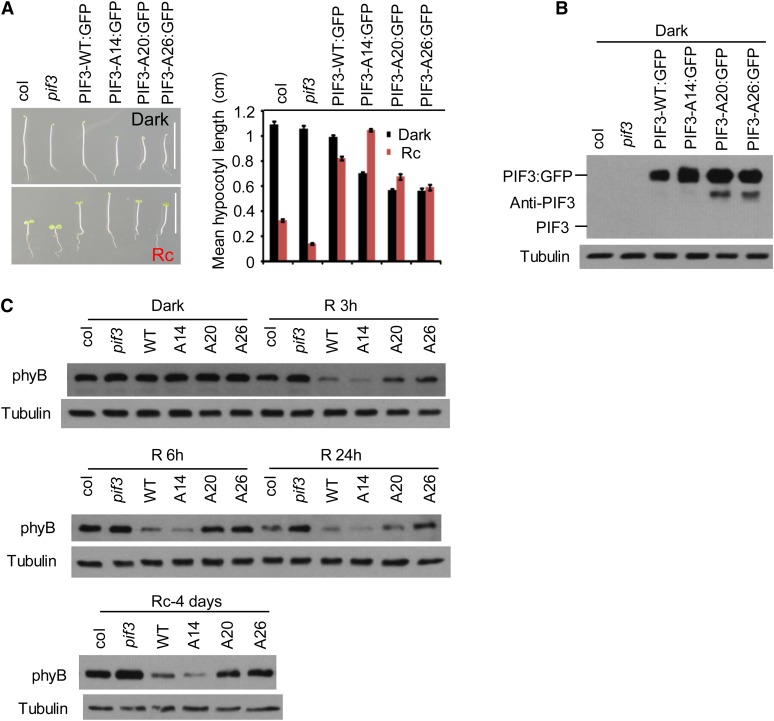
(A) The PIF3-A20 and PIF3-A26 transgenic lines are not as tall as the PIF3-WT and PIF3-A14 lines in prolonged continuous R light. Left panel: Four-day-old seedlings transgenically expressing PIF3:GFP fusions of the various PIF3 variants indicated in the pif3 mutant are shown in comparison with the Col wild type and the pif3 mutant. Seedlings were grown either in the dark (top image) or continuous R light (Rc) (bottom image) for 4 d. Bars = 1 cm. Right panel: Mean hypocotyl lengths of the genotypes shown on the left. Approximately 30 seedlings of each genotype were used for each analysis. Error bars represent se.
(B) PIF3 protein levels in the various lines shown in (A). Proteins were extracted from dark-grown seedlings and subjected to immunoblot analysis using affinity-purified anti-PIF3 antibody. A longer exposure would be required to observe endogenous PIF3 (see Supplemental Figure 6C online). Tubulin was used as control.
(C) PIF3-A20 and PIF3-A26 transgenic lines retain more phyB protein in the R light than PIF3-WT and PIF3-A14 lines. phyB protein level in the same PIF3 transgenic lines as shown in (A) were analyzed by immunoblot using a monoclonal anti-phyB antibody or antitubulin antibody as a control. Top two panels: Three-day-old dark-grown seedlings were either kept in the dark or irradiated with continuous R light for 3, 6, or 24 h before protein extraction. Bottom panel: Seeds were grown in continuous R light for 4 d before protein extraction.