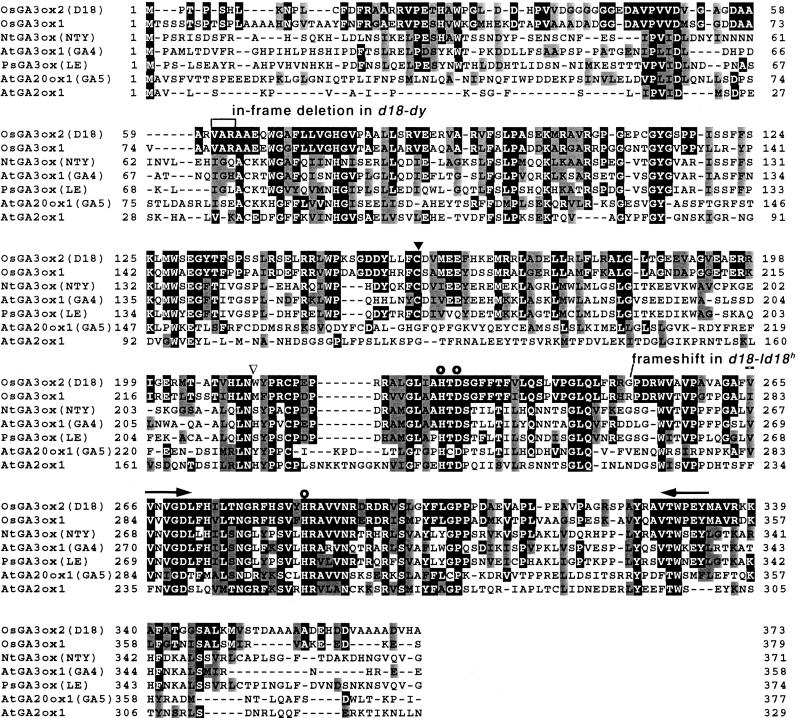
Figure 1.
Alignment of deduced amino acid sequences of GA 3β-hydroxylases and other GA dioxygenases from the monocot, rice, and several dicots. Alterations in the sequences from d18-Id18h and d18-dy are indicated. Light/dark shading indicates similar/identical residues. The three residues that are invariant throughout the plant 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases (whose side chains act as iron ligands) are marked with ○. ▾ indicates the position of the common intron in the rice 3β-hydroxylase genes; ▿ indicates the second intron in the OsGA3ox1 gene. Dashes indicate gaps introduced to optimize alignment. Arrows indicate the regions used in the design of degenerate primers. GenBank accession numbers are as follows: OsGA3ox1, AB054084; OsGA3ox2, AB056519; NtGA3ox, AB032198; AtGA3ox1, L37126; PsGA3ox, AF001219; AtGA20ox1, X83379; AtGA2ox1, AJ132435. Nucleotide sequences of OsGA3ox2 for d18-Id18h (accession number AB056517) and d18-dy (accession number AB056518) mutants are in GenBank. Recently, the nucleotide sequence of a P1 artificial chromosome clone that harbors OsGA3ox2 gene is registered in GenBank (accession number AP002523).