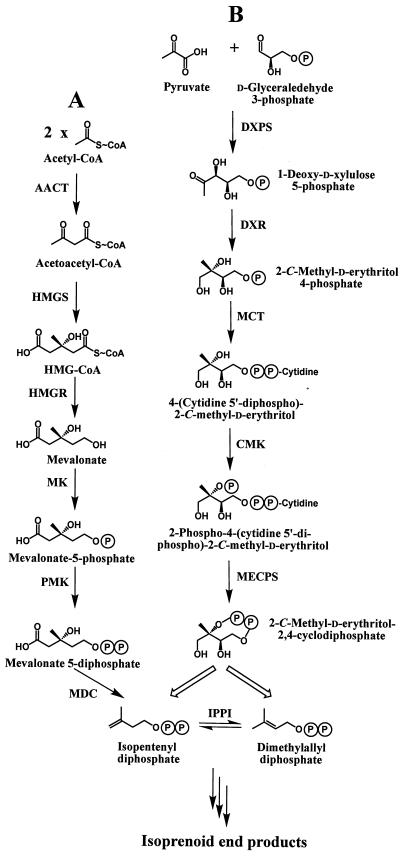
Figure 1.
Biosynthesis of IPP and DMAPP via the mevalonate pathway (A) and the mevalonate-independent (DXP) pathway (B). The indicated enzymes are: AACT, acetyl-CoA/acetyl-CoA C-acetyltransferase; HMGS, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase; HMGR, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase; MK, mevalonate kinase; PMK, phosphomevalonate kinase; MDC, mevalonate-5-diphosphate decarboxylase; DXPS, 1-deoxyxylulose-5-phosphate synthase; DXR, 1-deoxyxylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase; MCT, 2-C-methylerythritol-4-phosphate (MEP) cytidyltransferase; CMK, 4-(cytidine-5′-diphospho)-2-C-methylerythritol kinase; MECPS, 2-C-methylerythritol-2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase; and IPP isomerase (IPPI). The circled P denotes the phosphate moiety. The large open arrows indicate several as-yet-unidentified steps. The pathway may give rise to IPP and DMAPP independently (20) of the interconversion catalyzed by IPPI.