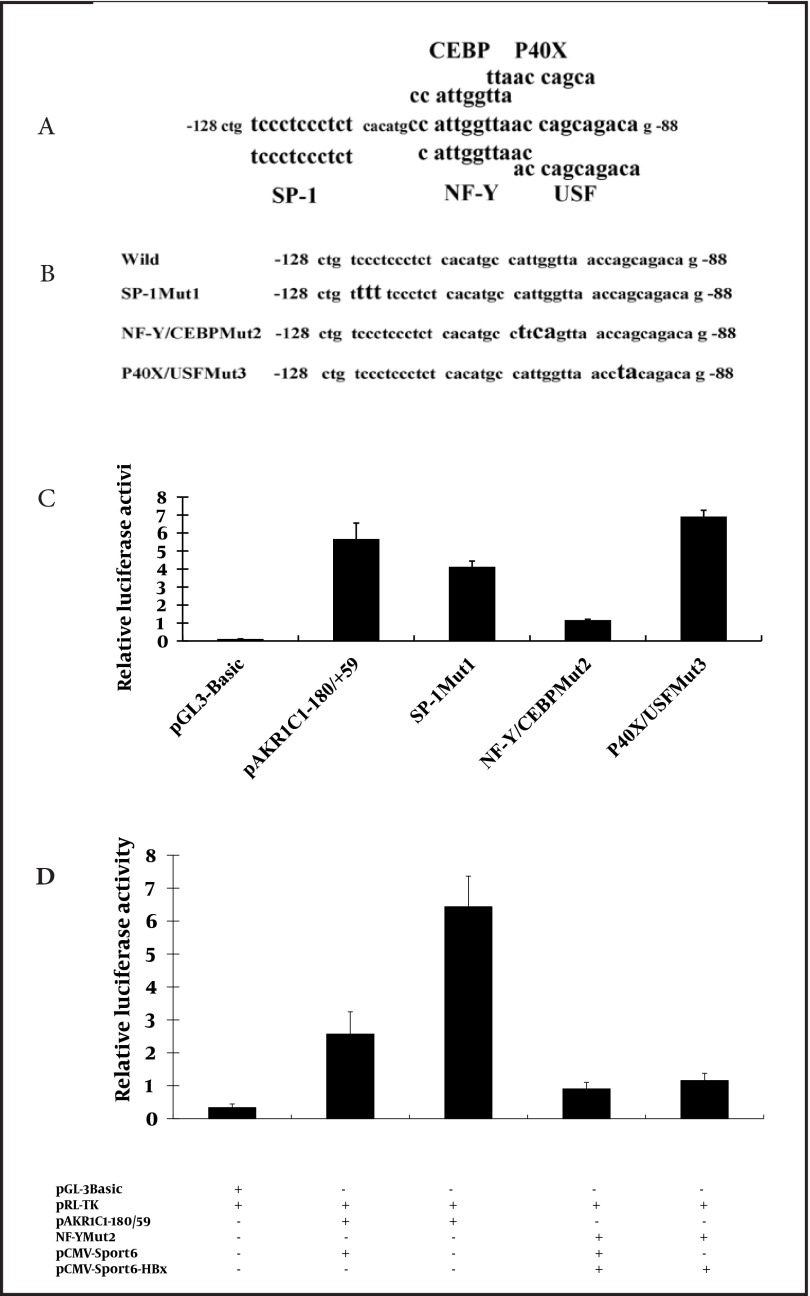
Figure 5. HBx Activated the AKR1C1 Expression in a NF-Y-dependent Manner.
A) The Alibaba 2.0 software and the TFSEARCH database was used to analyze the AKR1C1 promoter region between -128 and -88 and the potential transcription factor’s binding sites were identified. B) Three different mutants were obtained as described in materials and methods. Mut1 targeted the binding sites for the transcription factor SP1; Mut2 targeted the binding sites for the transcription factor NF-Y and CEBP; Mut3 targeted the p40X and USF binding site. C) HepG2.2.15 cells were transfected with pAKR1C1-180/+59Mut1, pAKR1C1-180/+59Mut2, pAKR1C1-180/+59Mut3, or the wild-type promoter (pAKR1C1-180/+59) and assayed for luciferase activity after 48 h. Transfection efficiency was normalized by co-transfection with pRL-TK. D) pAKR1C1-180/+59, NF-YMut2, and pCMV-sport6-HBx were co-transfected into HepG2 cells, pCMV-sport6 was used as the control and luciferase assay was performed. Transfection efficiency was normalized by co-transfection with pRL-TK. The mean ± SD are from three different experiments, each experiment performed in triplicate. *, P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 as compared with pCMV-Sport6 groups