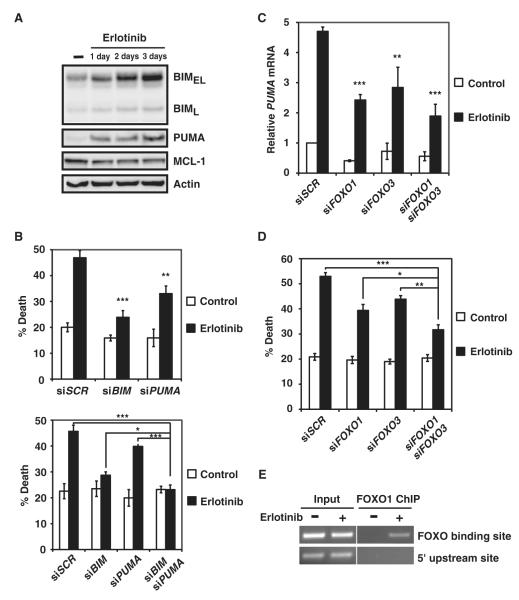
Fig. 4.
BIM and PUMA are required for erlotinib-induced apoptosis of EGFR-addicted lung cancer cells. (A) HCC827 cells, untreated or treated with erlotinib, were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies (n = 3 independent experiments). (B) Quantification of cell death by FACS analysis after annexin V staining of HCC827 cells transfected with scramble siRNA (siSCR) or siRNA against BIM and/or PUMA and left untreated or treated with erlotinib. Data are mean percentages of annexin V–positive cells ± SD from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. (C) PUMA mRNA abundance was assessed in HCC827 cells transfected with scramble siRNA (siSCR) or siRNA against FOXO1 and/or FOXO3 and left untreated or treated with erlotinib. Data are normalized against GAPDH and are means ± SD of three independent experiments. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. (D) Quantification of cell death by FACS analysis after annexin V staining of HCC827 cells transfected with scramble siRNA (siSCR) or siRNA against FOXO1 and/or FOXO3 and left untreated or treated with erlotinib. Data are mean percentages of annexin V–positive cells ± SD from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. (E) HCC827 cells, untreated or treated with erlotinib, were subjected to ChIP with the anti-FOXO1 antibody, followed by PCR amplification of the PUMA promoter. A 5′ sequence located 4 kb upstream of the transcription start site of PUMA served as a negative control (n = 2 independent experiments).