Figure 1. Schematic plot of the social media networks, where the items could be photos (as in Flickr), reviews (as in Epinions), videos (as in YouTube), etc.
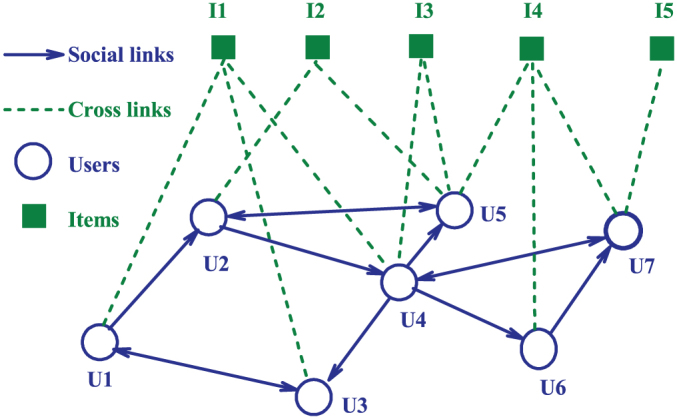
In principle, the social links (solid lines with arrowheads) are directional, while the cross links (dashed lines) are not. For these two types of links, we can define four types of degrees (see Methods for the details). For example, U4 in the network has indegree (kin = 2), outdegree (kout = 4), and favorite degree (kf = 2); I4 has popular degree (kp = 3). If the directions of social links are ignored, as we will do in the model, the links among users define the social degree (which is not the direct summation of indegree and outdegree because there is overlap between them for a user). In this case, for example, U4 has social degree (ks = 5) and favorite degree (kf = 2).
