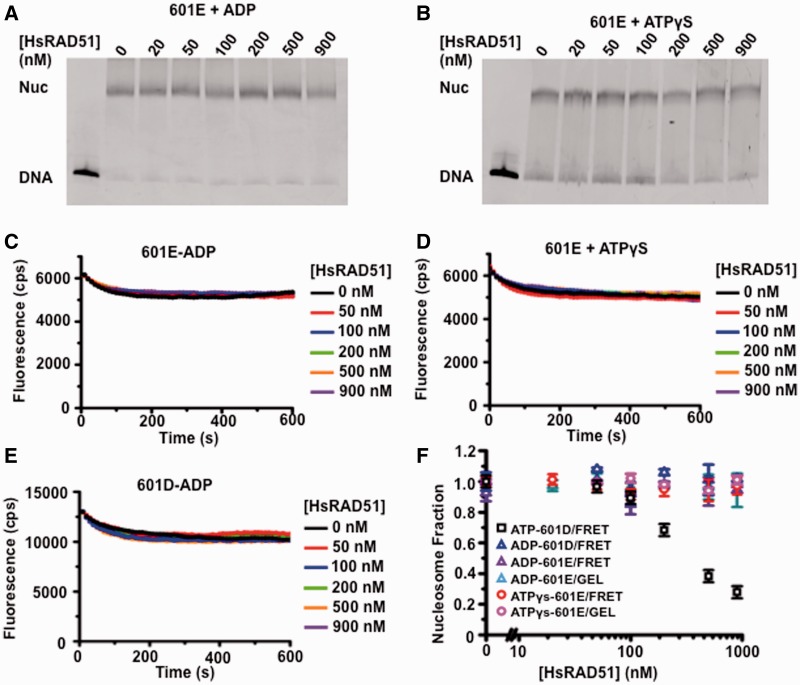
Figure 4.
The adenosine nucleotide dependence of HsRAD51 nucleosome disassembly. (A) Gel analysis of 601E nucleosome disassembly in the presence of ADP. The 601E nucleosomes (10 nM) were incubated with indicated concentration of HsRAD51, 130 mM KCl, ADP (250 µM) and 2 mM MgCl2 (Mg2+). (B) Gel analysis of 601E nucleosome disassembly in the presence of ATPγS. The 601E nucleosomes (10 nM) were incubated with indicated concentration of HsRAD51, 130 mM KCl, ATPγS (250 µM) and 2 mM Mg2+. (C) Representative FRET fluorescence decay of 601E nucleosomes (12 nM) incubated with HsRAD51 at 0 (black), 50 (red), 100 (blue), 200 (green), 500 (orange) and 900 nM (purple) in the presence of 130 mM KCl, ADP (250 µM) and 2 mM Mg2+. (D) Representative FRET fluorescence decay of 601E nucleosomes (12 nM) incubated with HsRAD51 at 0 (black), 50 (red), 100 (blue), 200 (green), 500 (orange) and 900 nM (purple) in the presence of 130 mM KCl, ATPγS (250 µM) and 2 mM Mg2+. (E) FRET analysis of 601D nucleosome disassembly in the presence of ADP. The 601D nucleosomes (12 nM) were incubated with indicated concentration of HsRAD51, 130 mM KCl, ADP (250 µM) and 2 mM Mg2+. (F) Quantitative analysis of the calculated nucleosome fractions of 601D from gel and FRET nucleosome disassembly analysis (Panel A–E) compared with the nucleosome fraction of 601D determined by FRET in the presence of ATP (Figure 3C). Color-coded key is shown in the inset. Standard deviation was calculated from at least two independent experiments.