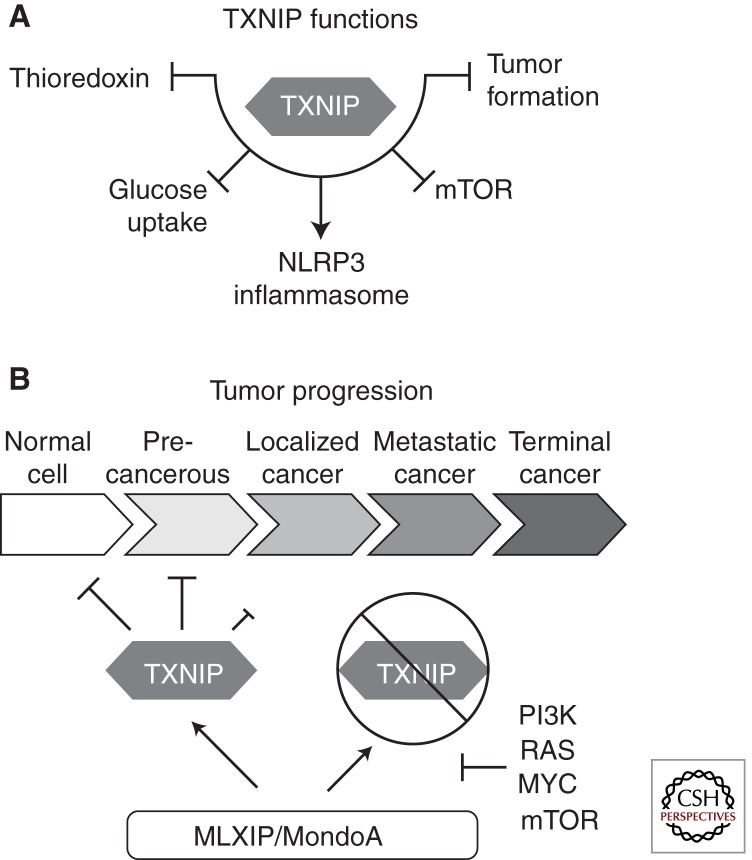
Figure 2.
Cellular roles for TXNIP. (A) TXNIP functions in numerous contexts within the cell. Prominent roles include inhibition of the redox protein thioredoxin (TXN), restricting glucose uptake through multiple potential mechanisms, inhibition of mTOR signaling via REDD1 stabilization, and restricting tumor formation. (B) MLIXP-TXNIP signaling serves to restrict cell growth via a metabolic or stress checkpoint. Disruption of this regulatory circuit is one potential mechanism that cells use to transition to an unrestricted growth phenotype, commonly found in cancer cells.