Figure 2. Wing modifications obtained in the P generation.
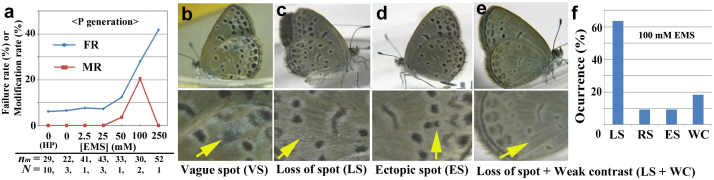
Note that these modified individuals were rare and were not used to generate offspring. Unique two-letter codes are assigned to all of the modification types. (a) The failure rate (FR) and the modification rate (MR). The number of trials (N) and the mean number of individuals (larvae) per trial (nm) are indicated (thus, these numbers are different from those of normal eclosion shown in Supplementary Table 2). HP indicates the host plant (i.e., natural diet, or ND). The MR increases dose-dependently up to 100 mM, but the FR also increases. (b) Vague-spot (VS) type. This individual was obtained by feeding 50 mM EMS. (c) Loss-of-spot (LS) type. In this individual, a particular spot was lost. This and other individuals shown here (c–e) were obtained by feeding 100 mM EMS. (d) Ectopic-spot (ES) type. (e) Loss-of-spot (LS) and weak-contrast (WC) types. (f) The occurrence of modification types obtained by feeding 100 mM EMS. RS indicates reduction-of-spot type (see phenotype shown in Figure 4). Total number of modified individuals was 8, but because double count was allowed when an individual shows two modifications traits, total number of counts was 11, as shown in Supplementary Tables 2 and 3.
