Fig 3.
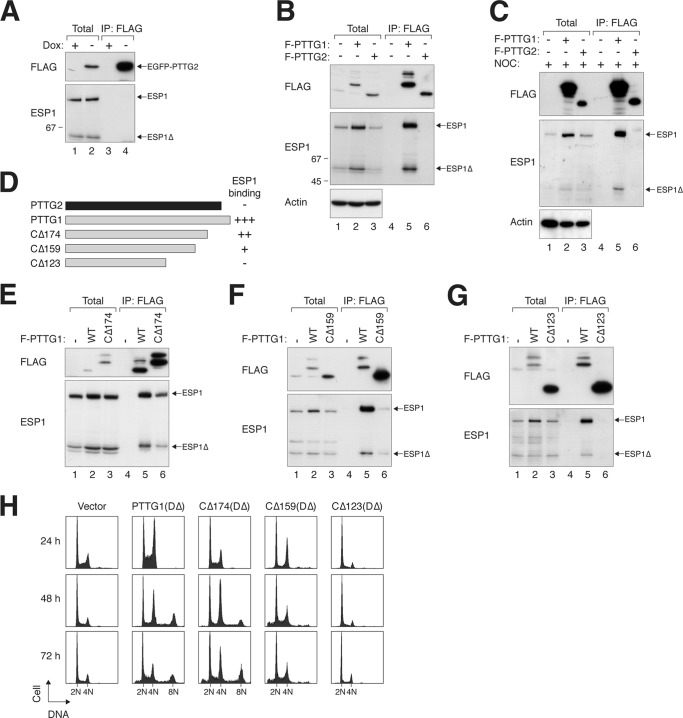
A C-terminal region of PTTG1 is required for interaction with separase. (A) PTTG2 does not interact with ESP1. A cell line expressing PTTG2 (FLAG-EGFP tagged) was transfected with ESP1-expressing plasmids. The cells were cultured in the absence or presence of doxycycline to turn PTTG2 on or off, respectively. Lysates were prepared and subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) with FLAG antibodies. After elution with FLAG-tagged peptides, the supernatant (together with total lysates) was analyzed by immunoblotting. The positions of full-length and cleaved ESP1 (ESP1Δ) are indicated. (B) PTTG1, but not PTTG2, interacts with ESP1. Cells were transfected with ESP1- and FLAG-tagged PTTG1 (F-PTTG1)- or PTTG2-expressing plasmids as indicated. Immunoprecipitation and subsequent immunoblotting were performed as described for panel A. As a control, no ESP1 was immunoprecipitated when it was expressed in the absence of FLAG-containing proteins. (C) PTTG2 does not interact with ESP1 during mitosis. ESP1was coexpressed with FLAG-tagged PTTG1 or PTTG2 as indicated. The cells were treated with NOC for 16 h to trap them in mitosis. Lysates were prepared and subjected to immunoprecipitation with FLAG antibodies. After elution with FLAG-tagged peptides, the supernatant (together with total lysates) was analyzed by immunoblotting. The positions of full-length and cleaved ESP1 (ESP1Δ) are indicated. (D) The C-terminal region of PTTG1 is involved in interacting with ESP1. A schematic diagram of PTTG1 deletion constructs is shown (to scale). The numbers indicate the positions beyond which the amino acid residues of PTTG1 were deleted (full-length PTTG1 is 202 residues long). A summary of ESP1 binding is also shown. (E to G) The C-terminal region of PTTG1 is required for interaction with separase. FLAG-tagged full-length PTTG1 and PTTG1CΔ174 (E), PTTG1CΔ159 (F), or PTTG1CΔ123 (G) were coexpressed in HeLa cells. Lysates were prepared and subjected to immunoprecipitation with FLAG antibodies. After elution with FLAG-tagged peptides, the supernatant (together with total lysates) was analyzed by immunoblotting. PTTG1CΔ174 migrated more slowly than PTTG1 because of extra sequences from a cloning artifact at the C terminus. WT, wild type. (H) The C-terminal region of PTTG1 is required to promote mitotic defects. HeLa cells were transfected with plasmids expressing DΔ versions of PTTG1 or C-terminally truncated PTTG1. Histone H2B-GFP was used as a cotransfection marker. The cells were harvested at the indicated time points and analyzed by flow cytometry (only transfected cells were analyzed). Cells with impaired sister chromatid separation underwent cytokinesis failure and became tetraploids.