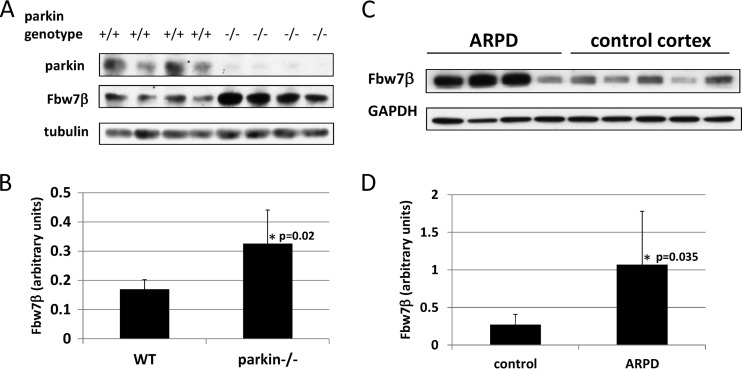
Fig 3.
Analysis of Fbw7β levels in mouse and human brains. (A) Extracts from whole brains of age-matched wild-type (+/+) and parkin-nullizygous (−/−) mice were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting for Fbw7β and parkin. (B) Quantitation using ImageJ of experiment shown in panel A. Fbw7β was normalized to tubulin. (C) Brain cortex extracts from four autosomal-recessive Parkinson's disease patients with a biallelic PARK2 mutation and five cortical extracts from normal brains were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting for Fbw7β. The third and fifth control samples correspond to different extracts prepared from the same cortex. The loading control was glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH). (D) Quantitation using ImageJ of experiment shown in panel C. Fbw7β was normalized to GAPDH. All error bars correspond to standard deviations. P values were determined using Student's t test.