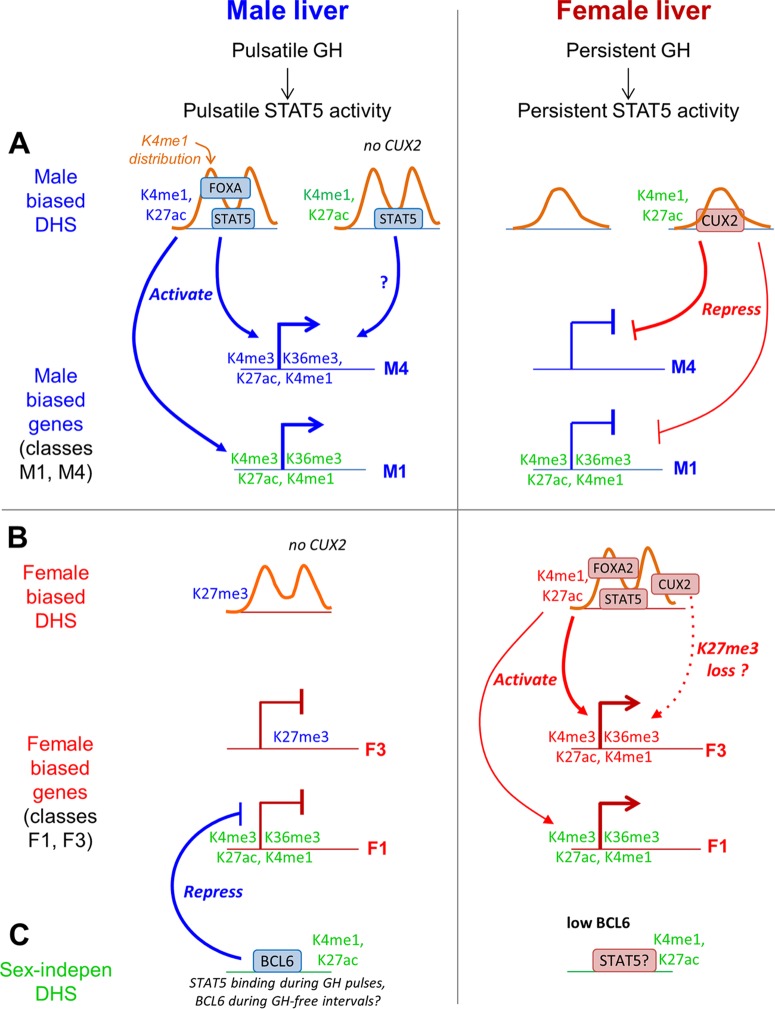
Fig 8.
Model for role of GH-regulated TFs and chromatin states in sex-biased gene expression in male liver and female liver. The model describes the two largest classes of sex-biased genes, which lack local sex-biased chromatin marks (class M1 with 267 genes and class F1 with 284 genes), and two classes of sex-biased genes with sex-biased local chromatin marks (class M4 with 17 genes and class F3 with 21 genes). Male-biased chromatin marks, genes, and TF binding sites are indicated in blue text; female-biased features are in red text; and sex-independent chromatin marks are in green text. Orange curves represent the distribution of K4me1 marks around DHS summits. (A) Male-biased DHS and genes. In male liver, male-biased DHS are marked by a bimodal distribution in K4me1 marks and by male-enriched K4me1/K27ac marks and are bound in a male-enriched manner by STAT5 and/or FOXA1/FOXA2. These DHS activate male-biased genes with local sex differences in chromatin marks (class M4) as well as genes that lack local sex differences in chromatin marks (class M1). In female liver, male-biased DHS exhibit a monomodal K4me1 distribution and are deficient in binding of STAT5 and in the binding of FOXA1/FOXA2, which facilitate male-biased DHS opening. CUX2 binding, which is restricted to female liver, is enriched at sites with sex-independent DHS/enhancer modifications and male-enriched STAT5 binding (34) and preferentially targets for repression class M4 male-biased genes and, to a lesser extent, the larger class M1 male-biased genes. (B) Female-biased DHS and genes. Female-biased DHS exhibit a bimodal K4me1 distribution in both male and female liver, have female-enriched enhancer modifications, and show female-enriched binding by STAT5, FOXA2, and CUX2. These three TFs preferentially target female-biased genes with sex differences in local chromatin marks (class F3 genes) and could act in a cooperative manner. CUX2 activation of class F3 and other female-biased genes may be facilitated by removal of K27me3 marks, which are enriched at these genes in male liver. (C) Sex-independent DHS. The male-biased repressor BCL6 shows enriched binding at sex-independent DHS that have sex-independent enhancer modifications, and it preferentially represses female-biased genes that lack local sex differences in chromatin marks.