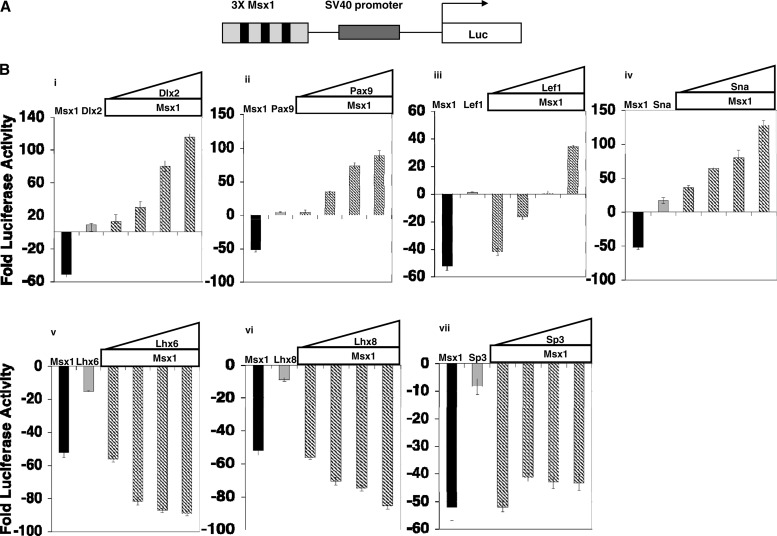
Fig 8.
Functional consequences of the interaction of Msx1 with tooth-specific transcription factors for the transcriptional regulation of an artificial Msx1-dependent promoter. (A) Schematic representation of reporter plasmid containing 3 Msx1 binding sites (3× Msx1). (B) C3H10T1/2 cells were cotransfected with 1 μg of reporter plasmid containing 3× Msx1-Luc, along with increasing amounts of expression plasmid Msx1-FLAG (0.25 μg, 0.50 μg, 0.75 μg, and 1.0 μg). Cells were harvested 24 h after transfection for reporter gene assays. Transcription efficiencies were determined using Renilla luciferase plasmid. For this and subsequent experiments, the levels of luciferase activity were normalized to Renilla luciferase activity and expressed as fold luciferase activity relative to the level of luciferase activity from cells transfected with the reporter construct and empty expression plasmid. Effects of Dlx2 (i), Pax9 (ii), Lef1 (iii), Sna (iv), Lhx6 (v), Lhx8 (vi), and Sp3 (vii) on Msx1-mediated transcription are shown. One microgram of the 3× Msx1-Luc reporter plasmid was cotransfected with 0.25 μg of Msx1-FLAG or 0.25 μg of the indicated transcription factor, or increasing amounts of transcription factors were added (0.25 μg, 0.50 μg, 0.75 μg, and 1.0 μg) along with 0.25 μg of Msx1-FLAG. All the transfection experiments were performed three times, and results are shown as means ± standard deviations. Pax9, Dlx2, Sna, and Lef1 acted as activators of transcription at the 3× Msx1 promoter in conjugation with Msx1, whereas Lhx8 and Lhx6 with Msx1 resulted in repression. The repression by Sp3 at the 3× Msx1 promoter did not change in the presence of Msx1.