Fig 4.
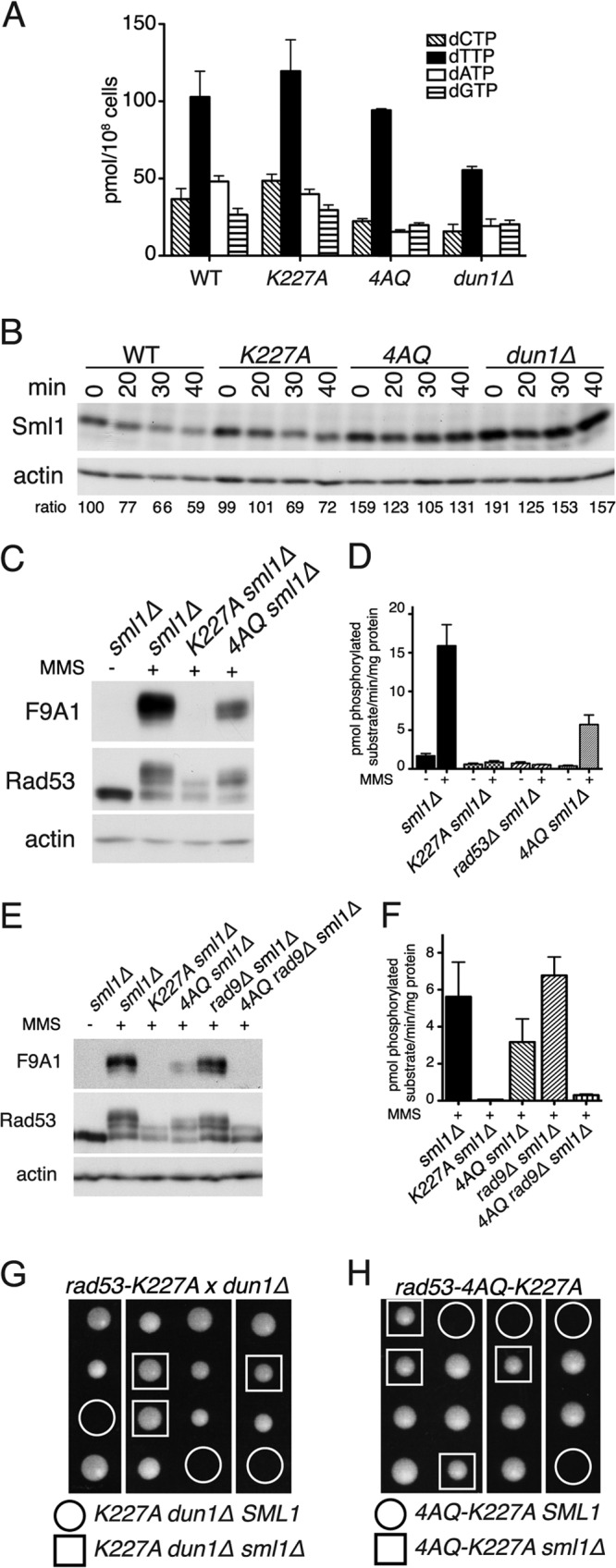
The rad53-4AQ phenotype reflects a combination of defective nucleotide regulation and impaired Rad53 kinase activation. (A) Measurement of endogenous dNTP pools in asynchronous cultures of the indicated strains (mean ± SEM; n = 2). (B) Western blot analysis of Sml1 levels in cells of the indicated genotypes at indicated times (min) after release from G1 arrest into YPD. Numbers below each lane are Sml1/actin ratios relative to those for WT G1, which was assigned an arbitrary value of 100. (C) Western blot analysis of the indicated strains after treatment with 0.05% MMS for 60 min (+) and untreated control. The F9A1 antibody is specific for activated Rad53 (28). (D) Rad53 IP kinase assay in indicated strains after treatment with 0.05% MMS for 60 min and untreated controls (mean ± SEM; n = 5 for WT−, WT+, K227A+, and 4AQ+; n = 2 for others). (E) Similar to panel C; Western blot analysis of the indicated strains after treatment with 0.05% MMS for 60 min. (F) Rad53 IP kinase assay of the indicated strains after treatment with 0.05% MMS for 60 min (mean ± SEM; n = 2). (G) Tetrad dissection of a diploid strain heterozygous for rad53-K227A, dun1Δ, and sml1Δ. (H) Tetrad dissection of a RAD53/rad53-4AQ-K227A SML1/sml1Δ diploid.
