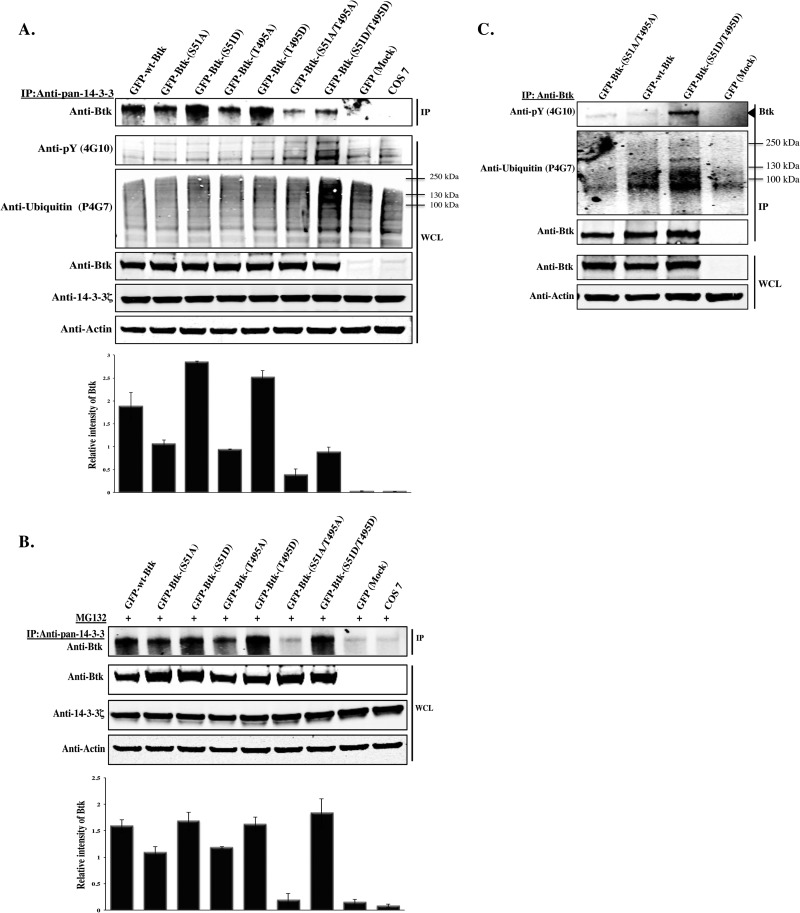
Fig 6.
S51- and T495-to-alanine substitution disrupts binding of Btk to 14-3-3ζ, while S51- and T495-to-aspartic-acid substitution promotes degradation. (A) Plasmids encoding GFP-Btk-wt and 14-3-3-binding-deficient mutants S51A, T495A, and S51A/T495A, as well as constructs encoding phosphomimetic mutants S51D, T495D, and S51D/T495D, were transfected into Cos-7 cells. Endogenous 14-3-3 was immunoprecipitated and probed with anti-Btk. WCL was immunoblotted with anti-pY (4G10), antiubiquitin (P4G7), anti-Btk, anti-14-3-3ζ, or antiactin antibody. (B) Ectopically expressed Btk was immunoprecipitated from whole-cell extracts of Cos-7 with anti-Btk antibody, and the precipitated proteins were detected with phospho-specific antibodies against global phosphoproteins (4G10) or with an antiubiquitin antibody (P4G7). Total Btk protein was detected by immunoblotting with anti-Btk. (C) Endogenous 14-3-3 proteins were immunoprecipitated with the anti-pan-14-3-3 antibody from Cos-7 cells transfected with Btk constructs and treated overnight with a proteasome inhibitor (MG132; 10 μm) and probed for the presence of Btk by immunoblotting with anti-Btk. Quantitative analysis of the top band in panels A and C was performed by densitometry analysis using Image J software. The data shown are representative of two independent experiments (the error bars indicate SE).