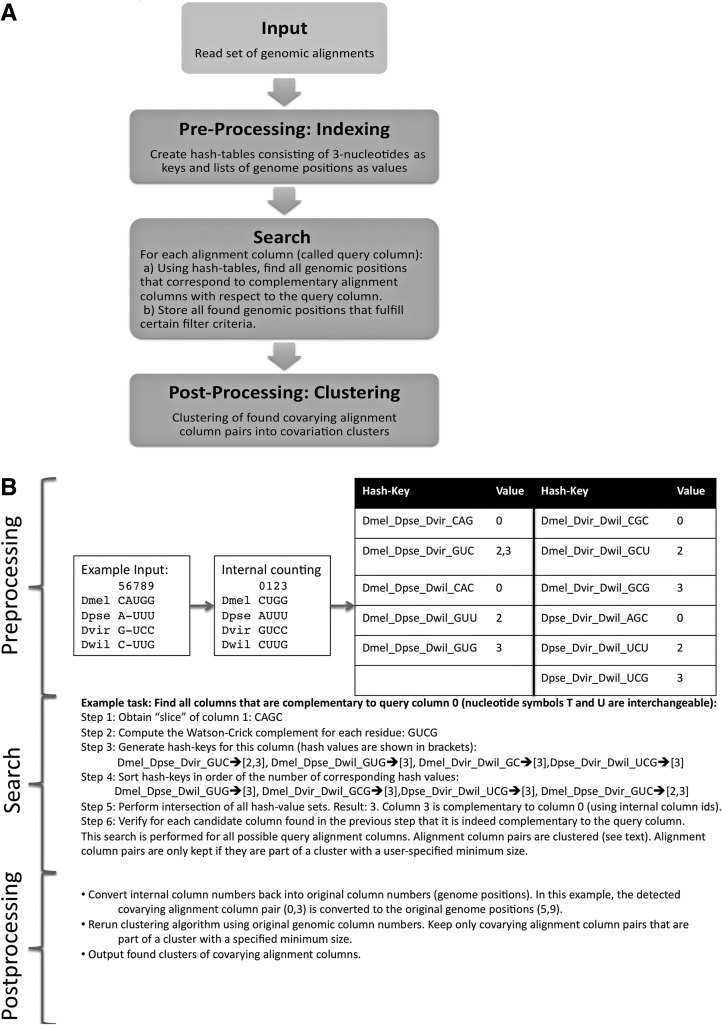
FIGURE 8.
Flowchart (A) and example (B) of CovaRNA search for covarying alignment columns. The approach can be divided in a pre-processing stage, a search stage, and a post-processing stage. Pre-processing: The original genomic alignment blocks (that might contain gaps, overlaps, and different strand directionalities) are consolidated leading to an unambiguous internal counting of column positions. Hash keys are generated corresponding to each possible genome triple and each possible nonconserved nucleotide triple. For each hash key, the alignment positions at which the three corresponding genomes exhibit the three corresponding nucleotides of the hash key are stored as the “value” of a hash map. Note that triples that are “conserved” (that is, the nucleotides corresponding to the three genomes of a triple are either AAA, CCC, GGG, or UUU) are not stored.