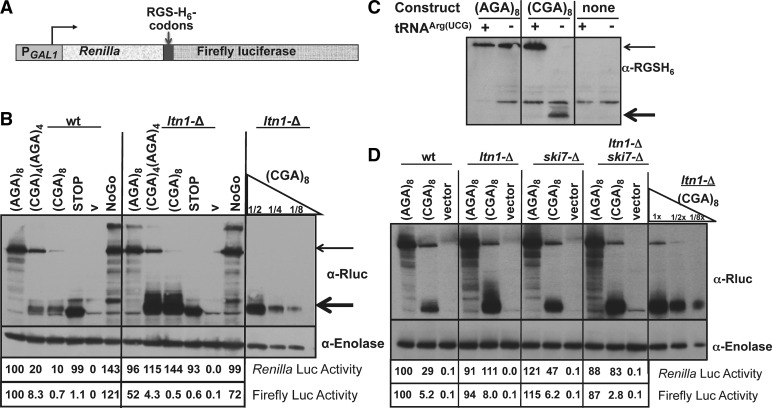
FIGURE 1.
Polypeptides arrested by CGA codons are targeted for degradation by the E3 ubiquitin ligase, encoded by LTN1. (A) Schematic of the Renilla-firefly luciferase fusion protein in which RGS-(His)6-(Arg)8 sequences are inserted at amino acid 314, and expression is under control of the GAL1 promoter. (B) Analysis of Renilla-firefly luciferase fusion protein expressed from the Renilla-RGS-(His)6-(Arg)8-firefly luciferase-reporter constructs under control of the GAL1 promoter, in either wild-type or ltn1-Δ yeast strains. The (Arg)8 insertion is specified by (AGA)8, [(CGA)4(AGA)4], or (CGA)8, as indicated above the panel. Luciferase fusion protein was detected with antibody directed against Renilla luciferase; antibody to enolase served as a loading control. Dilutions were performed with crude extracts expressing the (CGA)8 reporter constructs (12.5 μg, 6.3 μg, 3.1 μg). Firefly and Renilla luciferase activities of various reporter constructs all containing RGS-(His)6-(Arg)8 insertions were normalized to the (AGA)8 reporter construct in the wild-type strain. (C) Analysis of Renilla-firefly luciferase fusion protein in strains expressing the exact base-pairing variant tRNAArg(UCG) or a vector control. Strains used in the first four lanes bear constructs that are similar to those described in A except that expression is driven by PGK1 promoter, as described previously (Letzring et al. 2010). Strains in the last two lanes have no fusion construct. The fusion protein was detected with antibody directed against the RGS-(His)6 epitope. (D) Analysis of Renilla-firefly luciferase protein in reporter constructs containing RGS-(His)6-(Arg)8 insertions under control of the PGK1 promoter, from wild-type, ltn1-Δ, ski7-Δ, and ltn1-Δ ski7-Δ yeast strains bearing the indicated Arg codon insertions. Antibody detection and luciferase assays were done as described in B.