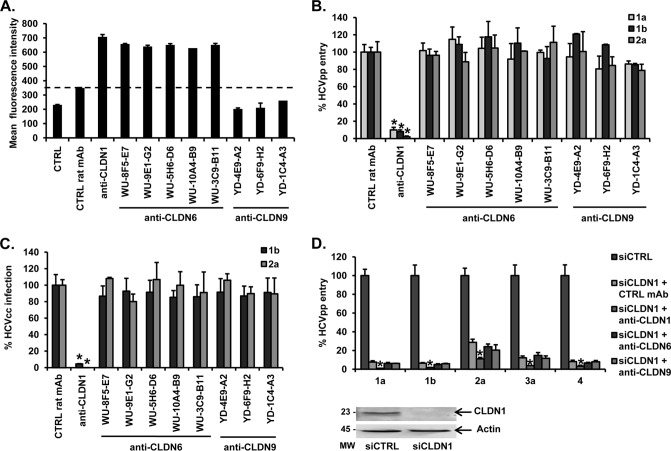
Fig 3.
CLDN6- and CLDN9-specific MAbs do not inhibit HCV infection in Huh7.5.1 cells. (A) Binding of CLDN-specific MAbs to Huh7.5.1 cells. Huh7.5.1 cells were detached and incubated with CLDN-specific MAbs. MAb binding (4 μg/ml) was revealed by flow cytometry using a CLDN1-specific MAb (OM-7D3-B3) as a positive control. Inhibition of (B) HCVpp entry or (C) HCVcc infection by CLDN-specific MAbs. Huh7.5.1 cells were preincubated for 1 h at 37°C with CLDN-specific or control MAbs (100 μg/ml) before infection with HCVpp (strains H77 [genotype 1a], HCV-J [1b], and JFH1 [2a]) or HCVcc (strains Luc-Con1 [genotype 1b/2a] and Luc-Jc1 [2a/2a]) for 4 h at 37°C. HCV infection was assessed by luciferase activity in cell lysates 72 h postinfection. (D) Inhibition of HCVpp entry in CLDN1-silenced (siCLDN1) Huh7.5.1 cells. CLDN1-silenced Huh7.5.1 (4) were preincubated for 1 h at 37°C with CLDN-specific or control MAbs (100 μg/ml) before infection with HCVpp (strains H77 [1a], HCV-J [1b], JFH1 [2a], UKN3A1.28 [3a], and UKN4.21.16 [4]). Western blot demonstrating CLDN1 silencing is indicated below; siCTRL, silencing control. Means ± SD from three independent experiments performed in triplicate are shown. Statistical analysis relative to the control MAb was performed using the Student t test; *, P < 0.05. MW, molecular weight in thousands.