Fig 1.
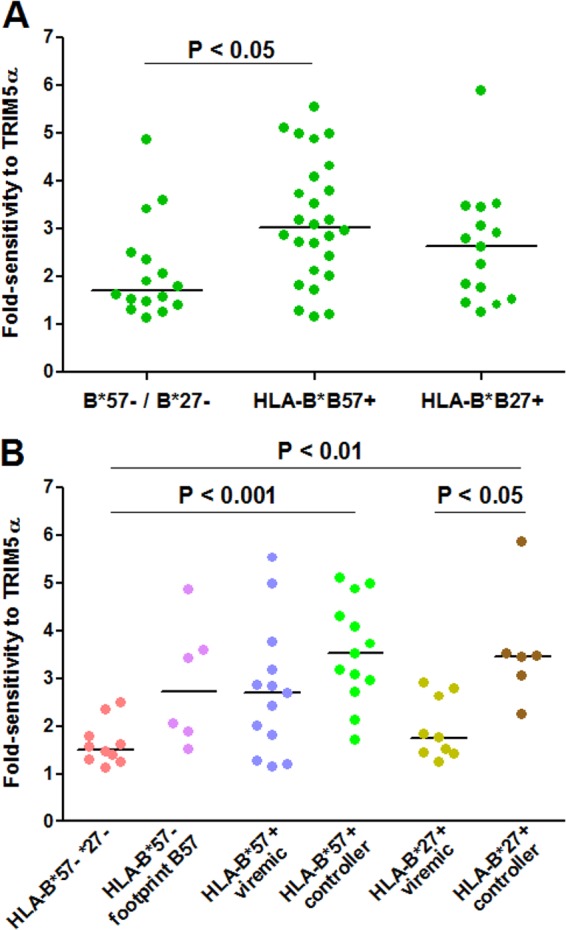
Sensitivity to hTRIM5α of recombinant viruses carrying CA sequences derived from plasma viruses. CA sequences of plasma viruses from HLA-B*57+ patients, HLA-B*27+, patients and HLA-B*57−/B*27− patients were amplified by RT-PCR, and amplification products were used to create recombinant viruses expressing Renilla luciferase in the place of Nef. Fold sensitivity to hTRIM5α was determined by measuring single-cycle infectivity using a luciferase-based assay after infection of U373-X4 cells in which hTRIM5α activity had been inhibited by stable overexpression of untagged hTRIM5γ (U373-X4-TRIM5γ) and in U373-X4 cells that express physiological levels of hTRIM5α (U373-X4-LacZ) and determining the ratio of these results. (A) Results for recombinant viruses from HLA-B*57+ (n = 26), HLA-B*27+ (n = 15), and HLA-B*57−/B*27− (n = 16) patients are compared. (B) Viruses from HLA-B*57− patients have been separated according to the presence or absence of 2 or more mutations associated with resistance to CTL targeting the 4 major epitopes in CA presented by HLA-B*57 (footprint B57). Viruses from HLA-B*57+ and HLA-B*27+ patients have been separated according to viral load in the absence of treatment (>500 copies/ml, viremic; <500 copies/ml, controller). Bars indicate medians. Statistical analysis: Mann-Whitney test (A) and Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn's multiple comparison test (B).
