Fig 6.
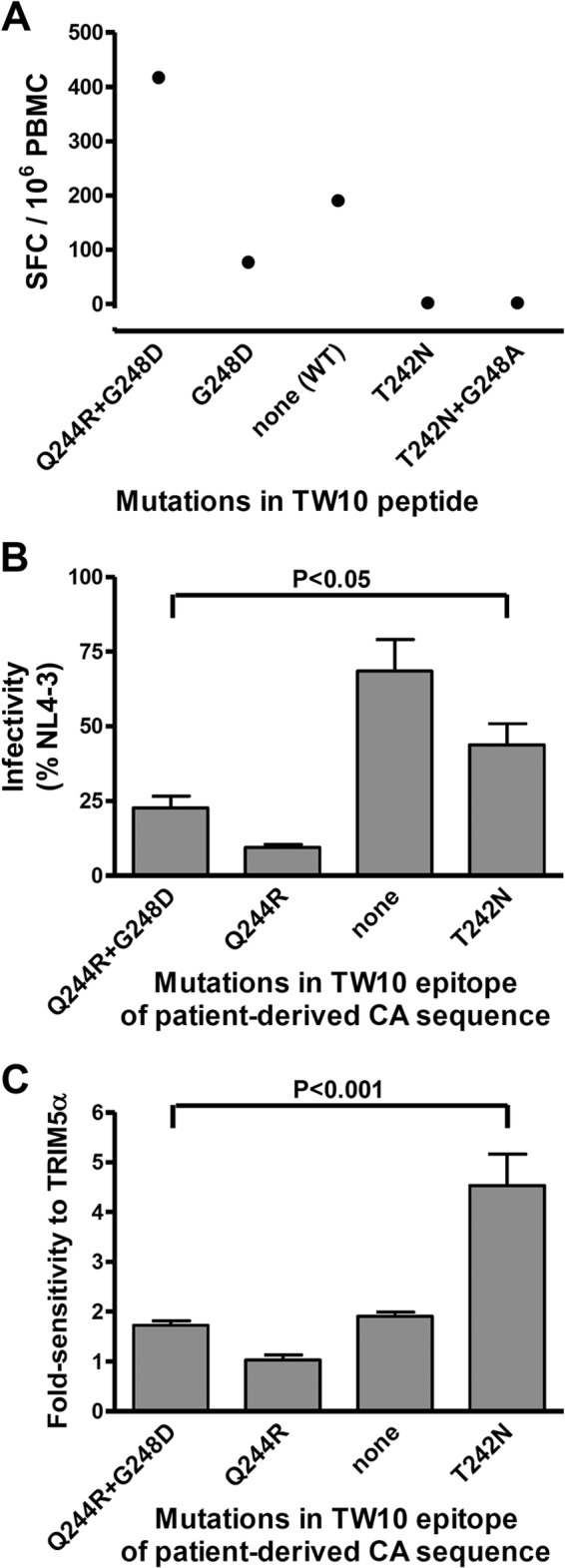
Effect of mutations in the TW10 epitope on CTL recognition, viral infectivity, and sensitivity to hTRIM5α. (A) PBMC from patient 57C3, who spontaneously controlled viral replication, were incubated with synthetic peptides having the consensus sequence of the TW10 epitope [TSTLQEQIGW, none (WT)] or peptides containing the indicated resistance mutations, and numbers of spot-forming cells (SFC) were measured using an IFN-γ-ELISPOT assay. (B) Recombinant viruses expressing Renilla luciferase in the place of Nef and carrying the CA sequence of viruses from the same patient (Q244R+G248D) and variants in which the indicated resistance mutations in the TW10 epitope had been added or removed were created. Single-cycle infectivity was measured using a luciferase-based assay after infection of U373-X4 cells in which hTRIM5α activity had been inhibited by stable overexpression of untagged hTRIM5γ (U373-X4-TRIM5γ). Results are expressed as a percentage of those obtained for a similar virus expressing the CA sequence of NL4-3. (C) The fold sensitivity to hTRIM5α of these viruses was also measured as described in the Fig. 1 legend. Results in panels B and C are the means ± SEM from 4 experiments performed using viruses obtained from two independent transfections. Statistical analysis was performed by analysis of variance followed by Bonferroni's multiple comparison test.
