Fig 1.
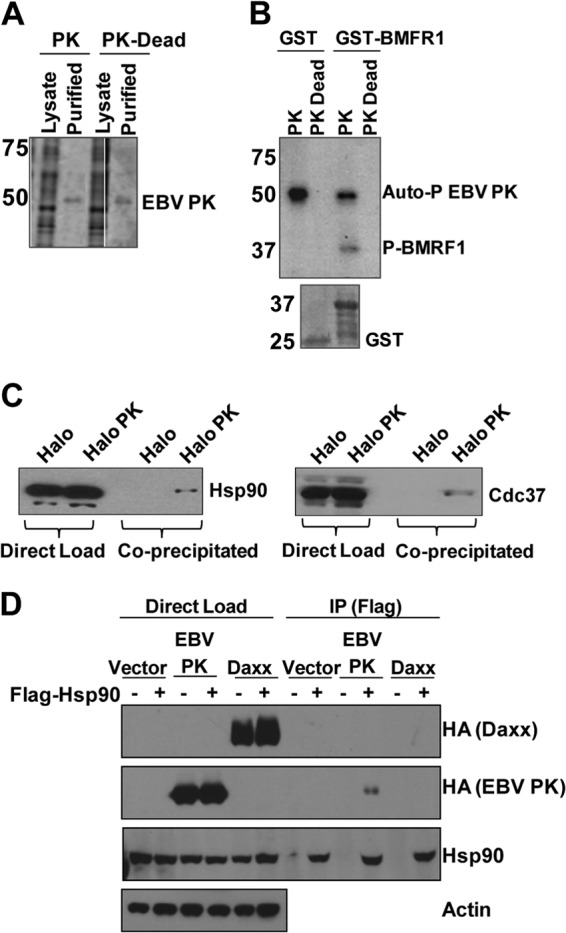
EBV PK associates with Hsp90 and Cdc37. (A) 293T cells were transfected with a vector expressing wild-type EBV PK fused in frame to a HaloTag or a kinase-dead mutant (PK-Dead), and the EBV PK proteins were then purified from the cell lysates (and cleaved from the tag). A Coomassie-stained gel showing the total cell lysate and purified EBV PK proteins is shown. (B) In vitro kinase assays using [32P]ATP were performed by using GST or GST-BMRF1 (C terminus) fusion protein and purified EBV PK proteins. (Top) Autoradiography showed phosphorylation of BMRF1 and EBV PK autophosphorylation, as indicated. (Bottom) A Coomassie stain of the GST proteins used for the kinase assay is also shown. Molecular weights (in thousands) are indicated on the left of panels A and B. (C) 293T cells were transfected with the Halo control vector or Halo-EBV PK, purified as described above for panel A, and immunoblotted with antibodies against Hsp90 (left) or Cdc37 (right). (D) HeLa cells were transfected with various combinations of the vector control, HA-tagged EBV PK, HA-tagged Daxx, and Flag-tagged Hsp90 expression vectors, as indicated, and then immunoprecipitated (IP) by using a FLAG antibody. Immunoblot analyses were performed to examine the expression of transfected proteins (direct load) or immunoprecipitated proteins by using HA, Hsp90, and actin antibodies.
