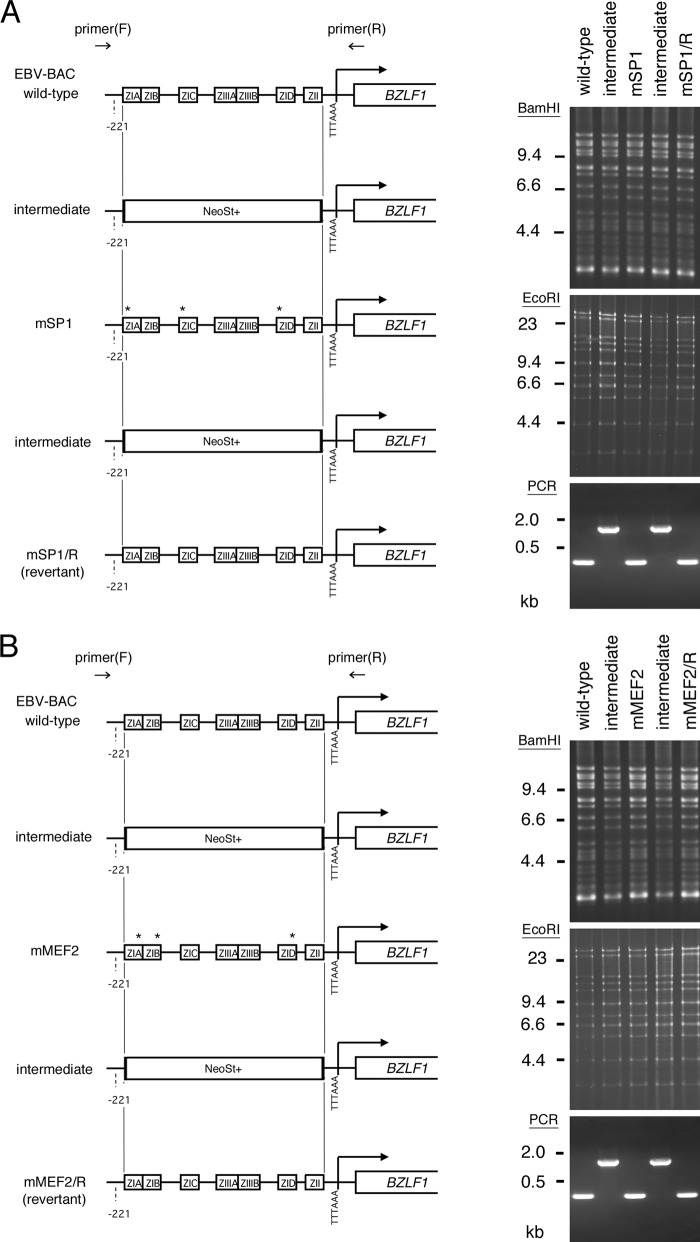
Fig 4.
Construction of recombinant EBV featuring point mutations in SP1 binding sites (A) and MEF2 binding sites (B) of the BZLF1 gene promoter. Shown is a schematic arrangement of the recombination of the EBV genome using tandemly arranged neomycin resistance and streptomycin sensitivity genes (NeoSt+). The BZLF1 promoter region was first replaced with the NeoSt+ cassette, which was then replaced with point-mutated sequences (asterisks) to construct EBV-BAC mSP1 or mMEF2. The mutated sequence was replaced again with the NeoSt+ marker cassette and swapped with the wild-type promoter sequence to prepare the revertant clone, EBV-BAC mSP1/R or mMEF2/R. The recombinant EBV genomes were digested with BamHI or EcoRI and separated in an agarose gel. PCR products produced by the indicated primers were electrophoresed to show successful recombinations.