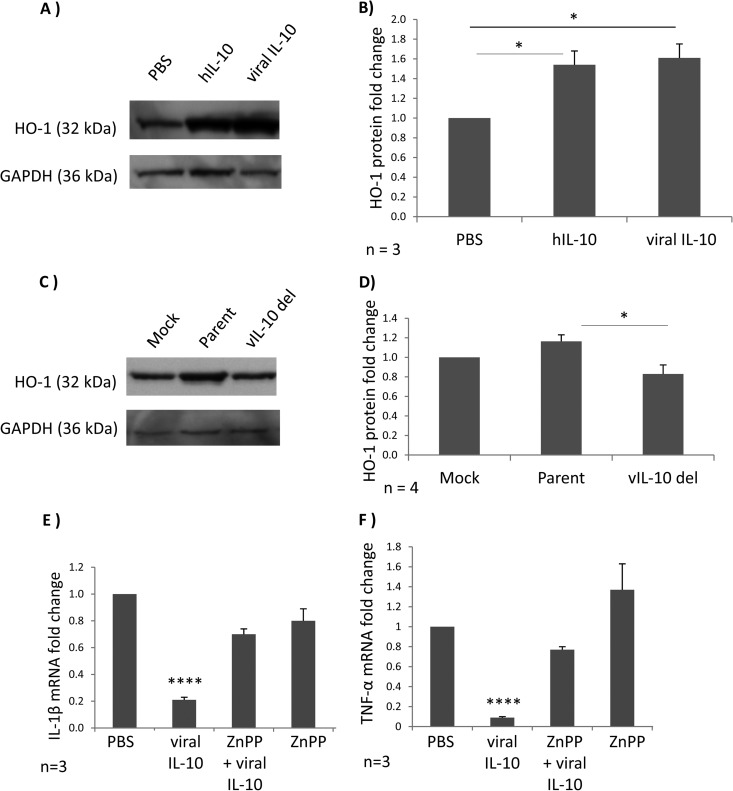
Fig 6.
Heme oxygenase 1 (HO-1) is upregulated in viral IL-10-polarized M2c monocytes and plays a role in viral IL-10-driven suppression of proinflammatory cytokines. (A) Western blot showing HO-1 protein levels in CD14+ monocytes treated with viral IL-10 (100 ng/ml), hIL-10 (100 ng/ml), or PBS (negative control) for 24 h. Expression of GAPDH was used as a protein loading control. (B) The fold change of HO-1 protein expression in monocytes treated with recombinant proteins was determined by densitometry normalized to the expression of GAPDH. (C) Western blot showing HO-1 protein levels in uninfected CD14+ monocytes cultured for 24 h with conditioned supernatants from HFF cultures productively infected with viral IL-10 deletion virus (vIL-10 del), parental virus (Parent), or with supernatants from mock-infected HFFs (Mock). Expression of GAPDH was used as a protein loading control. (D) The fold change of HO-1 protein expression in uninfected monocytes treated with supernatants was determined by densitometry normalized to the expression of GAPDH. Quantitative RT-PCR-based analysis of IL-1β mRNA (E) and TNF-α mRNA (F) in LPS-stimulated human CD14+ monocytes treated with viral IL-10 (100 ng/ml), with or without the HO-1 competitive inhibitor ZnPP (10 nmol/ml) is shown. Graphs depict fold change of mRNA expression relative to cells treated with PBS. Error bars indicate the standard errors of the means. Significant differences were determined using a one-tailed, paired Student t test: *, P < 0.05; ****, P < 0.0001.