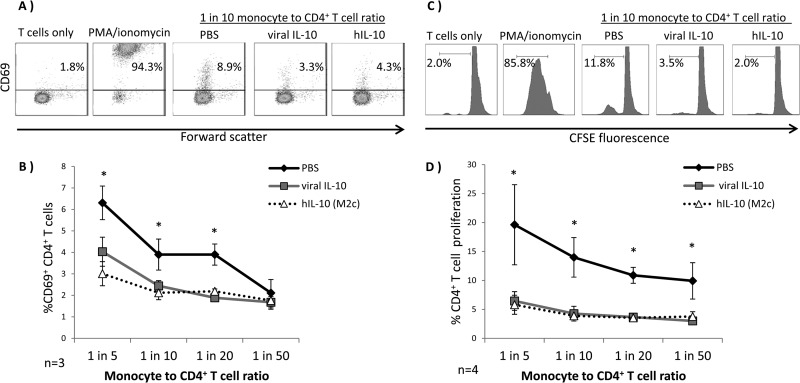
Fig 7.
CD4+ T cell activation and proliferation are inhibited by viral IL-10-polarized M2c monocytes in a mixed leukocyte reaction. Human CD14+ monocytes polarized with viral IL-10 (100 ng/ml) and hIL-10 (100 ng/ml) or with PBS (no polarization control) were cultured with CD4+ T cells in an allogeneic setting for 24 h prior to examination of an early T cell activation marker, CD69, or for 5 days with CFSE-labeled CD4+ T cells prior to assessment of CD4+ T cell proliferation by flow cytometry. CD4+ T cells with no monocytes added were used as a negative control while CD4+ T cells cultured with PMA-ionomycin were used as a positive control. (A) Representative flow cytometry scatter plots of CD4+ T cells expressing CD69. (B) Graph depicting the percentages of CD69+ CD4+ T cells. (C) Representative flow cytometry histograms showing percentage of proliferating CD4+ T cells. (D) Graph depicting the percentages of proliferating CD4+ T cells. The number of independent biological replicate experiments (n) is shown. Error bars indicate the standard errors of the means. Significant differences between viral IL-10- and hIL-10-treated samples compared to PBS-treated samples were determined using a one-tailed, paired Student t test (*, P < 0.05).