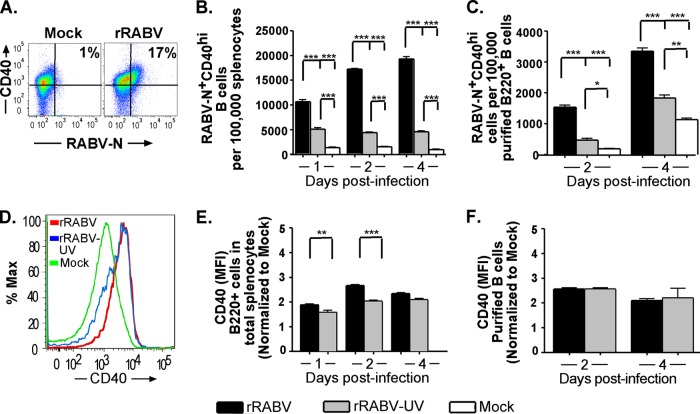
Fig 5.
B220+ mouse B cells from total splenocyte and isolated B cell cultures infected with rRABV upregulate surface expression of the survival and costimulatory molecule CD40. Cells cultured and infected as described in the legend to Fig. 1 were stained for surface B220 and CD40, as well as intracellular RABV-N, for analysis by flow cytometry. Data are from the same experiments and number of replicates per treatment described in the legend to Fig. 3. (A) Representative gating strategy of cells, as described in the legend to Fig. 3A, gated on surface CD40 and intracellular RABV-N staining. (B and C) Number of live RABV-N+ CD40hi B220+ B cells normalized to the number of live cells from total splenocyte cultures (B) or live B220+ cells from isolated B cell cultures (C) that were mock infected or infected in vitro with either rRABV or rRABV-UV at the indicated time points. (D) Representative histogram showing staining intensity of surface CD40 expression in live B220+ B cells from total splenocyte cultures infected in vitro with either rRABV or rRABV-UV or mock infected. (E and F) MFI of CD40 staining on live RABV-N+ B220+ B cells from total splenocyte cultures (E) or isolated splenic B cell cultures (F) infected in vitro with either rRABV (black bars) or rRABV-UV (gray bars), normalized to the MHC-II MFI of B220+ B cells from corresponding mock-infected cultures. To compare two groups of data, we used an unpaired, two-tailed Student's t test (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001).