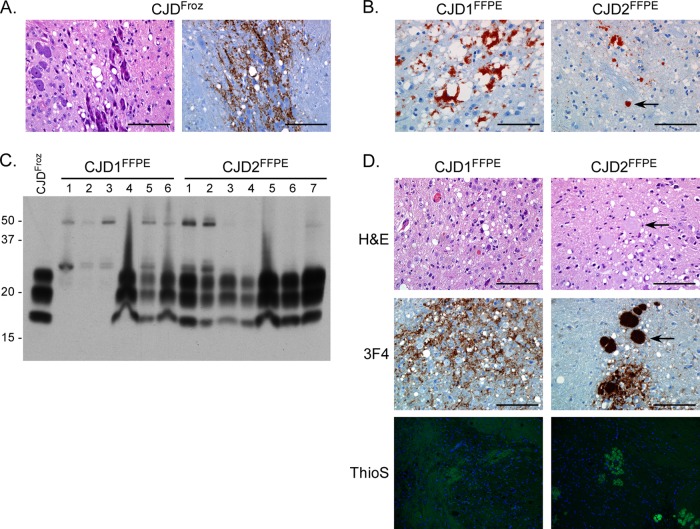
Fig 1.
Intracranial inoculation of FFPE sCJD brain tissue causes clinical or subclinical prion infection in Tg66 mice. (A) H&E (left panel)- and 3F4 (right panel)-stained sagittal sections from a clinically positive Tg66 mouse 167 days after inoculation with control CJDFroz brain homogenate. Spongiosis and PrPSc deposition (brown stain) are present in the pons. Scale bar, 100 μm. (B) Section of cortex stained with the anti-PrP monoclonal antibody 3F4 from a patient diagnosed with sCJD in 1979 (CJD1FFPE) or 1981 (CJD2FFPE). Both samples are positive for spongiosis and PrPSc (red stain). The arrow in the right panel indicates a unicentric PrPSc plaque. Scale bar, 100 μm. (C) Western blot analysis of brain homogenates from Tg66 mice inoculated with homogenates made from FFPE sCJD brain samples CJD1FFPE and CJD2FFPE. Each lane represents 0.7-mg brain equivalents of an individual mouse brain, except for the lane labeled CJDFroz, which represents brain homogenate from the sCJD MM type 1-positive control sample. The CJD1FFPE sample lanes 1 to 3 represent three mice that were euthanized for non-prion-disease-related causes at 113, 127, and 131 days postinfection. The blot was developed with the anti-PrP mouse monoclonal antibody 3F4 and the ECL development system. Molecular mass markers are indicated on the left. (D) H&E-, 3F4-, or Thioflavin S (ThioS)-stained sagittal brain sections from a Tg66 mouse at 234 (CJD1FFPE) or 648 (CJD2FFPE) days postinoculation with brain homogenate derived from FFPE sCJD brain samples. Spongiosis and PrPSc deposition (brown stain) are present in the midbrain in CJD1FFPE-inoculated mice and in the pons in CJD2FFPE-inoculated mice. The arrows in the top two right panels indicate a plaque visible in both the H&E- and 3F4-stained sections. ThioS-positive plaques were present only in animals inoculated with the CJD2FFPE sample. Scale bar, 100 μm.