Fig 2.
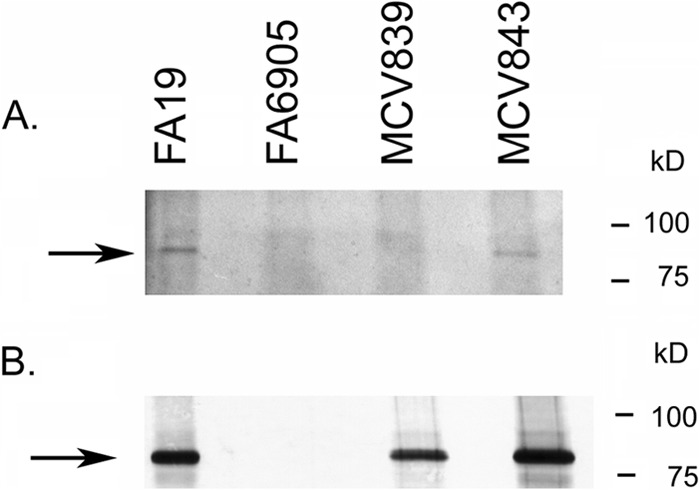
TbpB LSAC produced by MCV839 is not lipidated. (A) Gonococci were grown under iron-depleted conditions in the presence of azide-labeled palmitic acid. Bacteria were lysed, and azide-labeled proteins were conjugated to biotin alkyne (Click-iT labeling system; Invitrogen). Following separation by SDS-PAGE and transfer to nitrocellulose, proteins were probed with avidin-HRP, followed by detection with ECL. MCV839 (TbpB LSAC mutant) and MCV843 (TbpB ΔGly mutant) were tested for lipidation of TbpB, along with the control strains FA19 (wild type) and FA6905 (TbpB−). The arrow marks the location of full-length TbpB. Note that there is a lipidated protein slightly larger than TbpB which is apparent in all lanes. TbpB is produced and lipidated only in FA19 and MCV843. (B) The samples described for panel A were tested for production of TbpB by probing the blot with anti-TbpB serum, followed by goat anti-rabbit IgG secondary antibody conjugated to alkaline phosphatase. Bands were detected with NBT/BCIP. Approximate positions of molecular mass markers are shown on the right.
