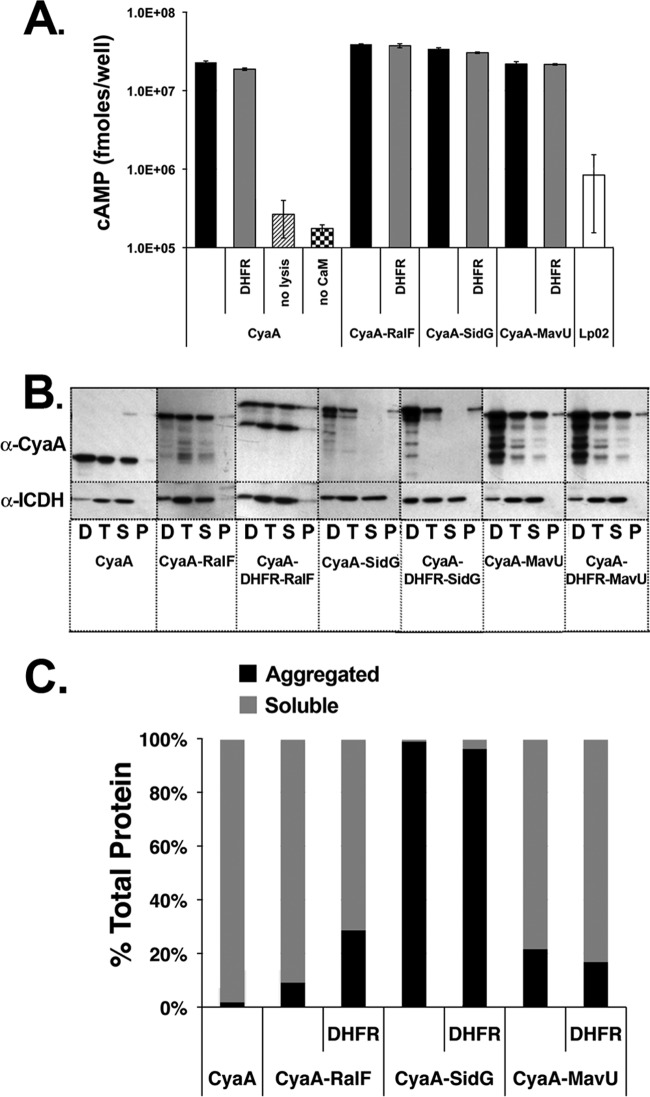
Fig 4.
Translocation deficiency is not due to loss of adenylate cyclase activity or aggregation of fusion proteins. (A) Adenylate cyclase activity is unaffected by DHFR. Bacterial lysates were incubated in the presence of ATP and calmodulin for 30 min at 37°C to allow for the production of cAMP. Samples were harvested and assayed as described in Materials and Methods. (B) Aggregation of IDTS protein fusions does not correlate with translocation defects of DHFR-IDTS fusions. L. pneumophila wild-type strains expressing the fusions were lysed, and cell debris was cleared by low-speed centrifugation. The resulting supernatant fraction was subjected to centrifugation at 90,000 × g for 1 h to precipitate any aggregated protein. Supernatant and pellet fractions after centrifugation were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-CyaA and anti-ICDH antibody probes. D, low-speed pellet; T, low-speed supernatant; S, high-speed supernatant; P, high-speed pellet. (C) The intensity of the fusion proteins in panel B was determined by densitometry, and protein expression is graphed as a percentage of the total protein after high-speed centrifugation.