Fig 5.
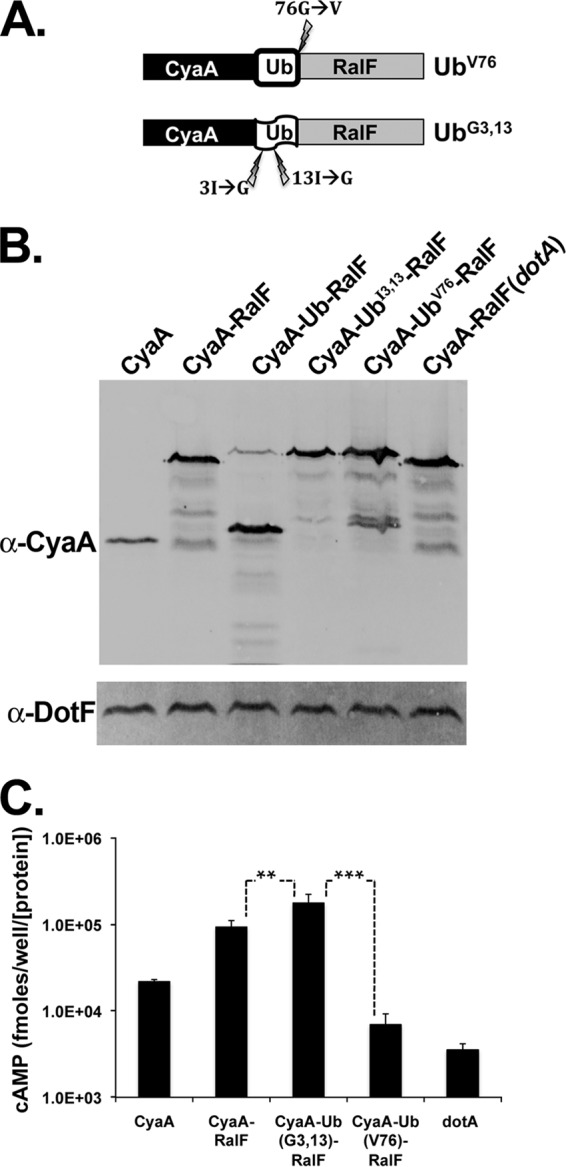
Folded ubiquitin inhibits translocation of fused Icm/Dot substrates. U937 cells were challenged with the wild-type L. pneumophila strain Lp02 or a translocation-defective dotA strain expressing CyaA-tagged RalF fused to either ubiquitin, a nonfolding variant of ubiquitin (UbG3,13), or a variant that cannot be cleaved by DUBs (UbV76). (A) Schematic of the RalF-Ub fusions. Lightning bolts indicate locations of the mutations used to create an uncleavable (UbV76) or destabilized (UbG3,13) ubiquitin. (B) Wild-type Ub is cleaved in L. pneumophila. Immunoblotting of fusion protein expression was performed using a monoclonal antibody against CyaA. Bacterial load was quantified using antibody against the Icm/Dot complex protein DotF. The blot is a representative of strains used in one typical CyaA translocation assay. (C) Folded Ub inhibits translocation. A CyaA translocation assay was performed as described in the legend of Fig. 1. The values represent the average cAMP amounts produced from four independent experiments (9 to 12 independent infections) normalized to DotF and then normalized to the expression of CyaA in the vector. Asterisks mark significance based on Student's t test (*, P ≤ 0.02; **, P ≤ 0.0002; ***, P ≤ 0.0009).
