Fig 7.
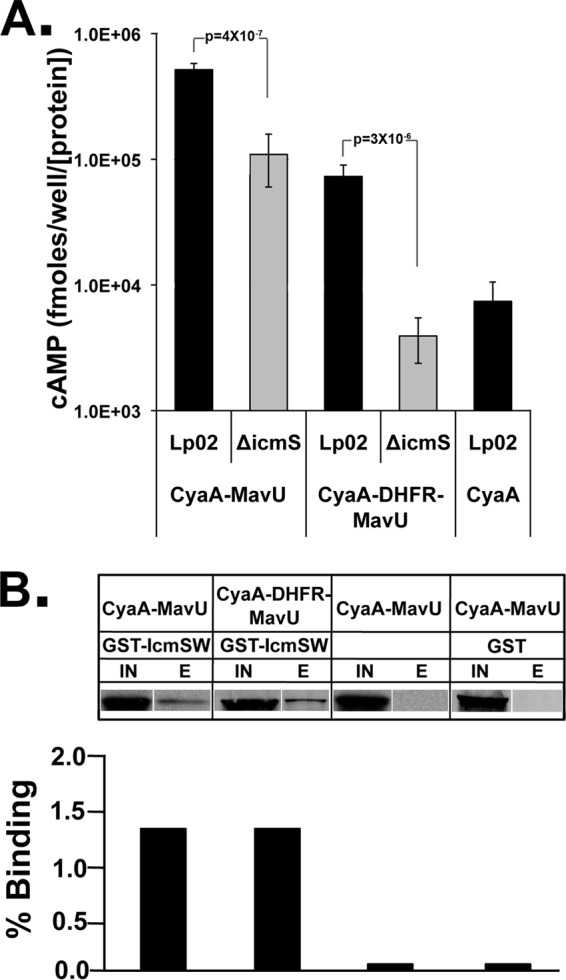
DHFR does not preclude interaction of the IcmS adapter protein with the IDTS protein fusions. (A) Lowered translocation of DHFR-MavU fusions to MavU in the absence of IcmS. CyaA-MavU and CyaA-DHFR-MavU were expressed in the wild-type strain (Lp02) and an IcmS-deficient strain (ΔicmS strain) and used to challenge U937 cells. A CyaA translocation assay was performed as described in the legend of Fig. 2. The values represent the average amount of cAMP determined by ELISA in five independent experiments (15 independent infections) normalized to the amount of the T4SS protein DotF expressed and then normalized to the amount of CyaA in the vector. (B) IcmS copurifies with MavU-DHFR fusions. Copurification of CyaA-MavU and CyaA-DHFR-MavU with GST-IcmS/W was performed. Lysates from E. coli encoding the indicated fusion with or without a second plasmid expressing GST or GST-IcmS/W were incubated with glutathione-conjugated resin for 1 h. Bound GST-IcmS and complexed proteins were eluted by reduced glutathione and concentrated by TCA precipitation. Protein samples were analyzed via Western blotting using anti-CyaA. Shown are the clarified lysate (IN) and the eluate concentrated 20-fold (E). The experiment was performed twice. The IN and E lanes from each sample were analyzed on a single blot but were loaded on noncontiguous lanes, as noted by gaps between lanes.
