Fig 8.
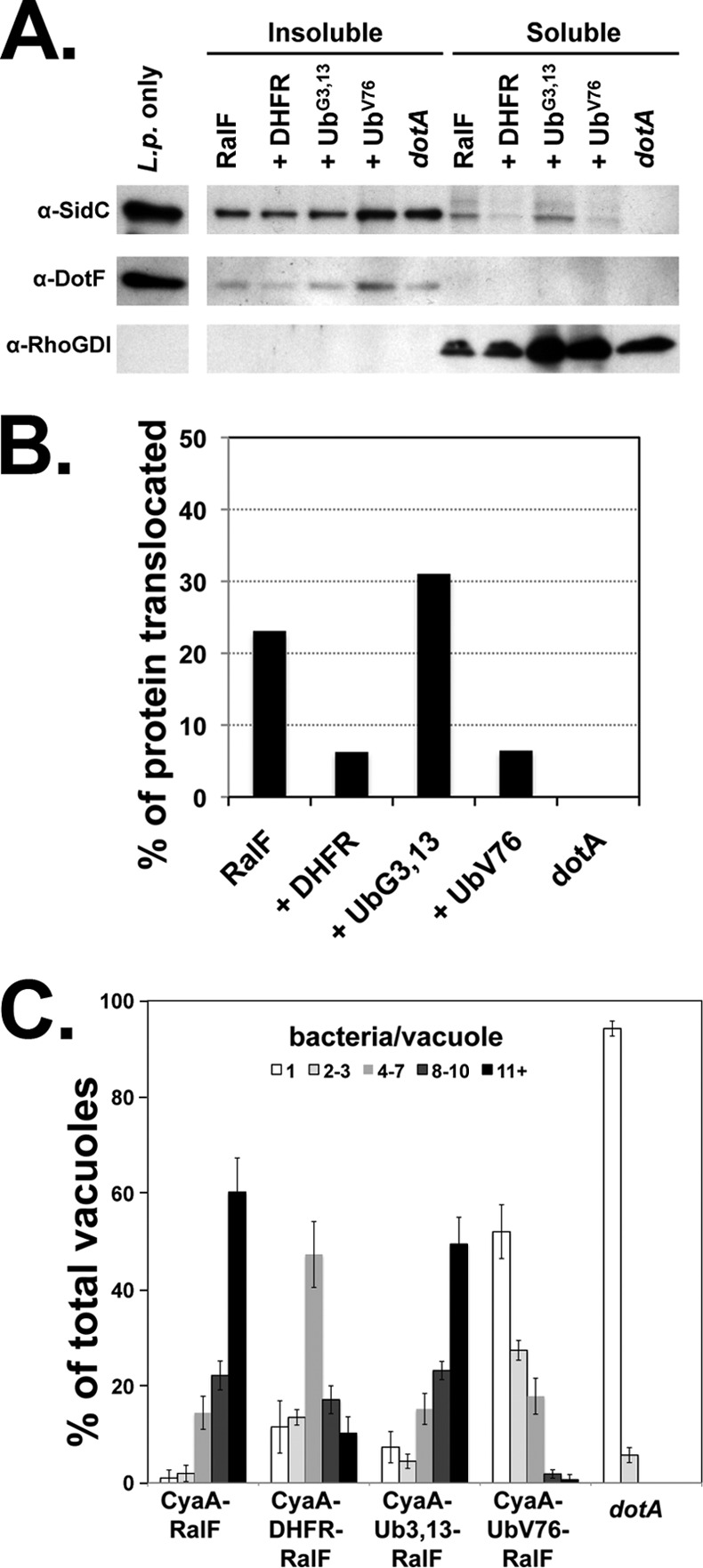
Folded protein fusions cause a partial blockage of the Icm/Dot translocon. (A) Translocation of SidC is decreased in strains harboring folded fusions. Secretion of IDTSs in strains overexpressing folded protein fusions was visualized by detergent fractionation of infected cells (see Materials and Methods). U937 cells were challenged with Legionella expressing CyaA-RalF fusions to DHFR, a folded Ub (UbV76), or the unfolded Ub (UbG3,13). After 1.5 h, cells were washed and lysed with 0.5% digitonin, and the soluble and insoluble fractions were separated by centrifugation. Translocation of the IDTS SidC into the cytoplasm of infected cells (digitonin-soluble extract) was analyzed by probing via immunoblotting. Antibodies to the bacterial T4SS protein DotF and the cytoplasmic protein RhoGDI were used to confirm that lysis does not release bacterial proteins as well as to show separation of the fractions. L.p., L. pneumophila. (B) The graph depicts the percentage of the SidC protein translocated, considered as the amount in the soluble fraction relative to the total protein in the sample, as determined by densitometry. The experiment was performed twice. Shown is a representative experiment. (C) Intracellular growth of strains harboring folded fusion proteins is inhibited. Murine bone marrow macrophages were challenged with either the wild-type strain (Lp02) or dotA strains harboring RalF fusions containing DHFR, a folded Ub (UbV76), or the unfolded Ub (UbG3,13). Growth was allowed to proceed for 14 h, at which time the infected macrophages were fixed and stained with an antibody against Legionella. The number of intracellular bacteria in individual vacuoles was determined for 100 cells each on three individual replicates for each sample. Data indicate the percentage of vacuoles with 1, 2 to 3, 4 to 7, 8 to 10, and 11 or more bacteria per vacuole ± standard error.
