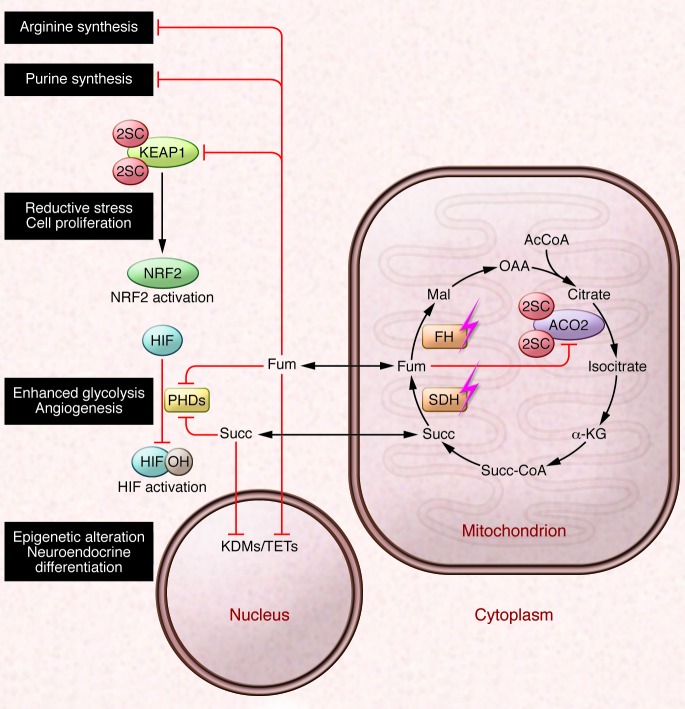
Figure 2. Candidate oncogenic mechanisms of succinate and fumarate accumulation.
SDH and FH are Krebs cycle enzymes and tumor suppressors. Loss-of-function mutations in SDH and FH result in abnormal accumulation of Krebs cycle metabolites succinate (Succ) and fumarate (Fum), respectively, both of which can inhibit the activities of α-KG–dependent oxygenases. Inhibition of HIF PHDs leads to activation of HIF-mediated pseudohypoxic response, whereas inhibition of KDMs and TET family of 5mC hydroxylases causes epigenetic alterations. Fumarate is electrophilic and can also irreversibly modify cysteine residues in proteins by succination. Succination of KEAP1 in FH deficiency results in the constitutive activation of the antioxidant defense pathway mediated by NRF2, conferring a reductive milieu that promotes cell proliferation. Succination of the Krebs cycle enzyme Aco2 impairs aconitase activity in Fh1-deficient MEFs. Fumarate accumulation may also affect cytosolic pathways by inhibiting the reactions involved in the biosynthesis of arginine and purine. AcCoA, acetyl CoA; Mal, malate; OAA, oxaloacetate; Succ-CA, succinyl CoA.