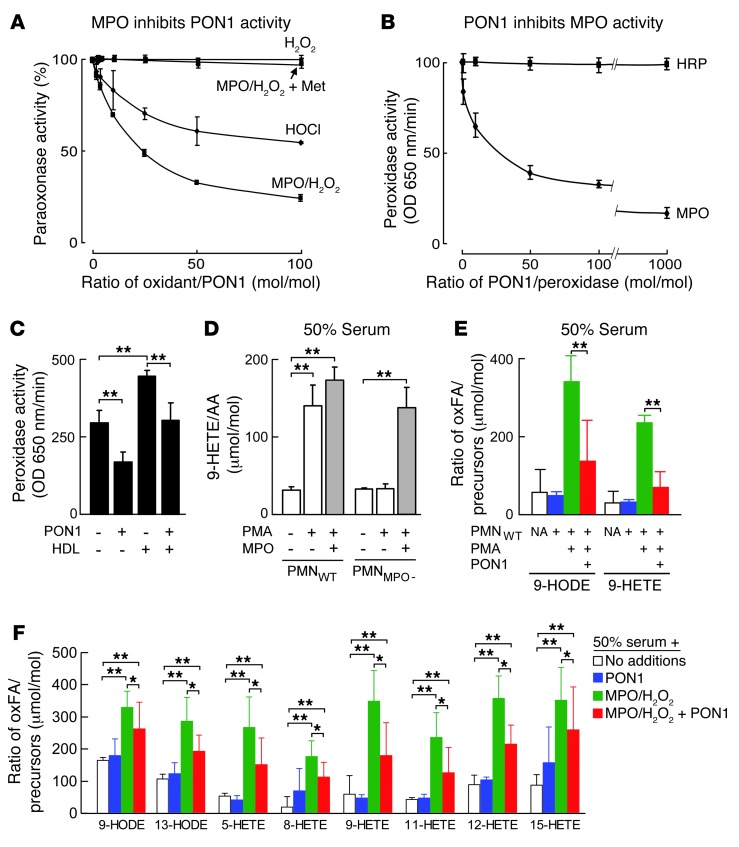
Figure 1. MPO and PON1 inhibit each other’s activity in vitro.
(A) PON1 (100 μg/ml) was incubated with either HOCl or H2O2 and MPO (50 nM) in 50 mM Na[PO4] buffer (pH 7.0) supplemented with isolated human HDL (1 mg/ml) and 100 mM NaCl at 37°C for 60 minutes. This was followed by quantification of paraoxonase activity relative to no oxidant exposures. Also shown are the effects of varying levels of H2O2 alone (i.e., no MPO added) or with the addition of the HOCl scavenger methionine (Met) (10-fold molar excess relative to oxidant) to the MPO/H2O2 system. (B) Effect of PON1 on peroxidase activity by TMB assay of either MPO or HRP. (C) Effect by TMB assay of PON1 (650 nM), HDL (650 nM), or both on MPO (65 nM) peroxidase activity. (D and E) Human neutrophils isolated from healthy donors (PMNWT) or MPO-deficient subjects (PMNMPO–) were incubated at 37°C in 50% serum for 1 hour in the absence or presence of phorbol 12-myristrate 13-acetate (PMA) and MPO or PON1, as indicated. Endogenous serum arachidonic acid (AA), linoleic acid (LA), 9-HODE, and 9-HETE were then quantified by stable isotope dilution LC/MS/MS as described in Methods. (F) PON1, MPO/H2O2, neither, or both were added to 50% serum, incubated at 37°C for 1 hour, and then AA, LA, or the indicated oxidation products were quantified as described in Methods. Data shown represent the mean ± SD of triplicate determinations. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.001. NA, no additions; oxFA, oxidized fatty acids.