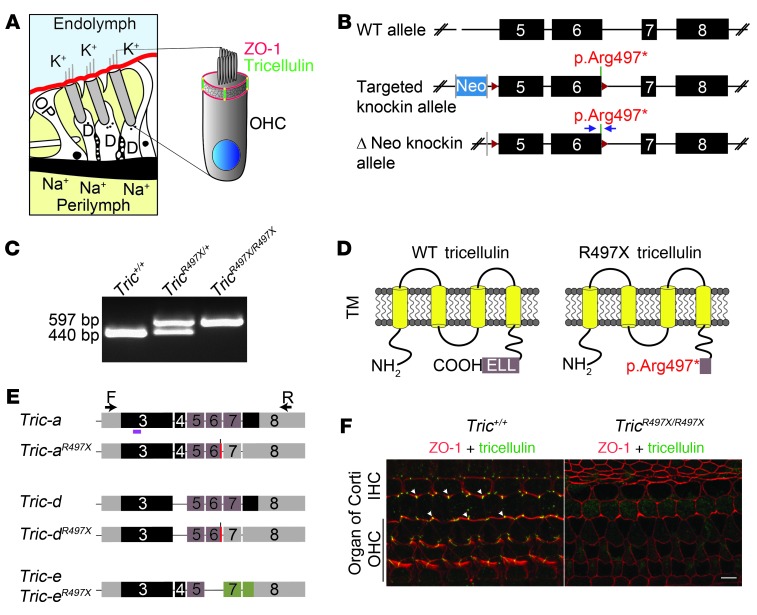
Figure 1. p.Arg497* mutation results in loss of tricellulin from the organ of Corti.
(A) Schematic of organ of Corti cross-section, showing the tight junctions that separate endolymph (blue) from perilymph (yellow). At tricellular junctions, tricellulin (green) spans the entire depth of the cuticular plate and intersects ZO-1 (red) at apical and basal ends of these junctions. OP, outer pillar cell; D, Deiters’ cell. (B) Scheme for generating the TricR497X/R497X mice. Exons 5 and 6 were flanked by LoxP (red arrowheads) sites, and the neomycin selection cassette (Neo) that was flanked by FRT sites (gray bars) was removed by crossing TricR497X/R497X mice with mice expressing Flp recombinase gene (59). The blue arrows represent the primers used to genotype the knockin mice. (C) PCR detection of wild-type allele (440 bp) and targeted allele (579 bp). (D) Schematic of the wild-type prematurely truncated tricellulin that is expected from the targeted allele. TM, transmembrane domain. (E) Schematics of transcripts (a, d, and e) that were amplified by RT-PCR from Tric+/+ and TricR497X/R497X inner ear cDNA and the location of the primers used for the reaction (arrows). Gray boxes indicate untranslated regions, and other colored boxes depict coding exons. Tric-a and Tric-d from TricR497X/R497X inner ear cDNA had the knockin mutation (red bars). Brown exons encode the occludin-ELL domain. The magenta bar shows the location of the peptide used to generate the tricellulin antibody, PB705 (24). (F) Tricellulin (green) is absent from tricellular junctions in the organ of Corti of TricR497X/R497X mice. Scale bar: 5 μm.