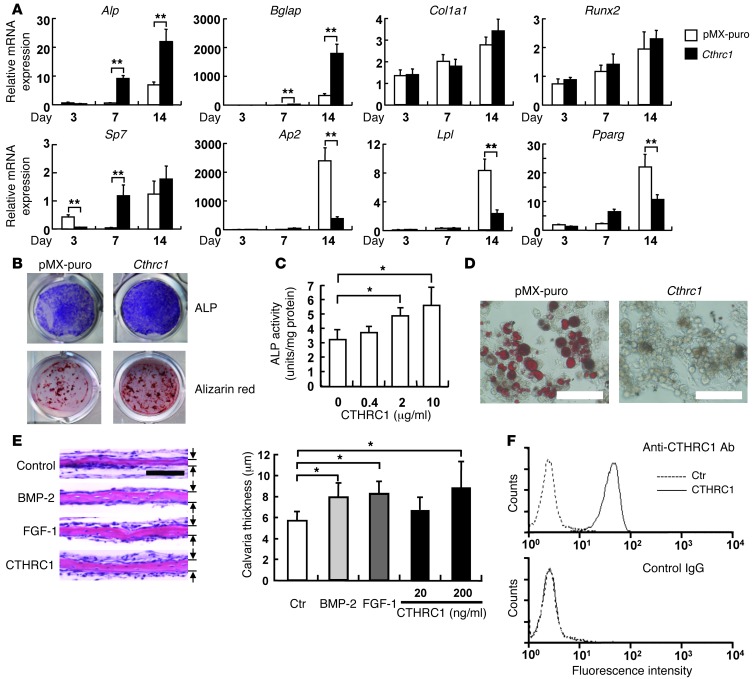
Figure 3. CTHRC1 stimulates osteoblastogenesis and bone formation.
(A) Retroviral transduction with Cthrc1 stimulated osteoblastogenesis and suppressed adipogenesis, as determined by gene expression. Calvarial osteoblastic cells were transduced with pMX-puro vector (white bars) or pMX-puro-Cthrc1 (black bars). On days 3, 7, and 14 after cells reached confluence, RNAs were extracted, and quantitative RT-PCR analysis was performed for expression of Alp, Bglap, Col1a1, Runx2, and Sp7 for osteoblastogenesis and Ap2, Lpl, and Pparg for adipogenesis. See Supplemental Table 1 for primers. n = 3. (B) Cells were stained for ALP and Alizarin red on days 7 and 14, respectively. (C) Recombinant mouse CTHRC1 protein stimulated ALP activity in ST2 cells dose dependently. n = 3. (D) CTHRC1 inhibited adipocyte differentiation from 3T3-L1 cells, as determined by Oil Red-O staining. Scale bar: 100 μm. (E) CTHRC1 stimulated bone formation in organ culture. Mouse calvaria was treated with recombinant CTHRC1 (20 and 200 ng/ml), BMP-2 (100 ng/ml), or FGF-1 (100 ng/ml), and bone-forming activity was assessed by measuring calvaria thickness (arrows). n = 3. Scale bars: 100 μm. (F) Binding of CTHRC1 to a putative receptor on ST2 cells. After treatment of ST2 cells with recombinant CTHRC1 protein (solid line) or PBS control (dashed line), cells were stained with rabbit anti-CTHRC1 polyclonal antibody (top) or rabbit IgG as a negative control (bottom) and PE-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG, then analyzed using flow cytometry. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.