Fig 7.
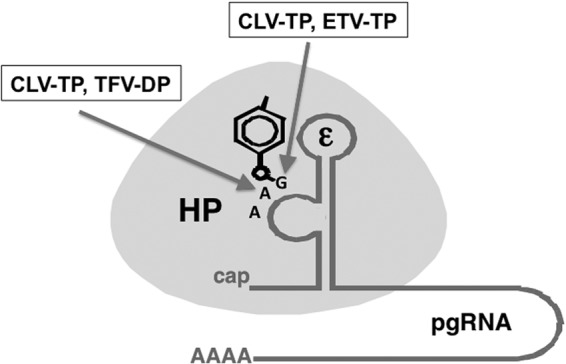
Summary of the inhibitory effects on HBV protein priming by NRTIs. HP is depicted as an oval and the viral RNA template (ε) for protein priming as a stem-loop structure with an internal bulge. As drawn, ε is part of the viral pgRNA with a 5′ cap and 3′ poly(A) tail. The phenol ring from Y63 in the RT protein, used to prime reverse transcription, is highlighted, as are the first three nucleotides of the viral minus-strand DNA that is covalently attached to HP as a result of protein priming. Both clevudine-TP (CLV-TP) and entecavir-TP (ETV-TP) are able to inhibit the initiation stage of protein priming (the covalent attachment of the first nucleotide, dGMP, to HP), and clevudine-TP (CLV-TP) and tenofovir DF-DP (TFV-DP) are able to inhibit the DNA polymerization stage of protein priming (the addition of two dAMPs following dGMP). See the text for details.
