Fig 5.
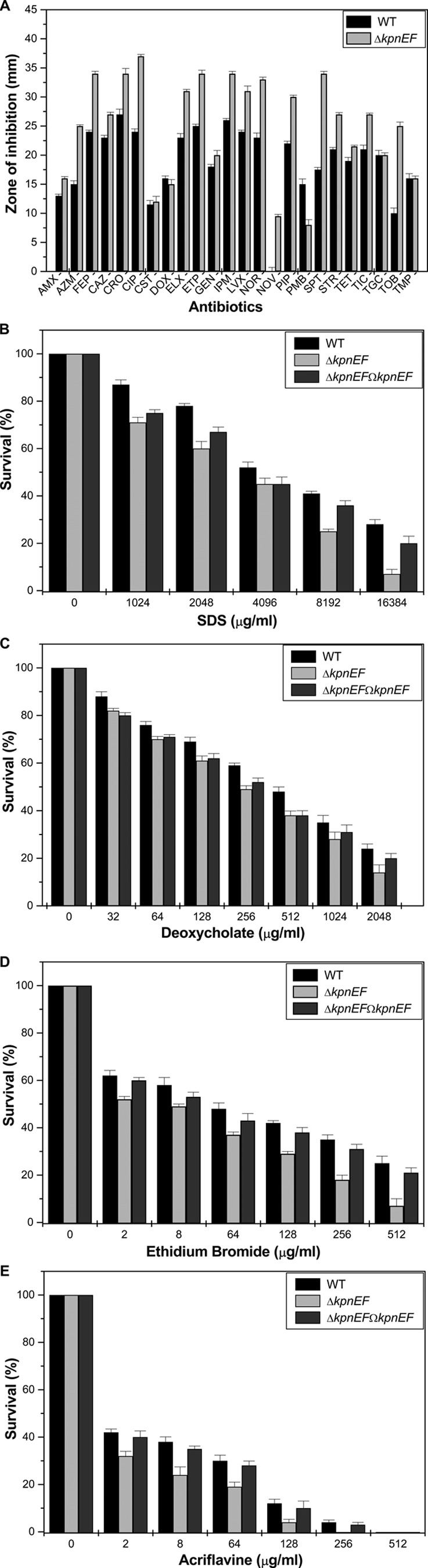
Contributions of the KpnEF efflux pump in K. pneumoniae antimicrobial resistance. (A) A Kirby-Bauer disc diffusion assay was performed with different antibiotics using commercial discs. Antibiotics, abbreviations, and concentrations: amoxicillin, AMX (30 μg/ml); azithromycin, AZM (15 μg/ml); cefepime, FEP (30 μg/ml); ceftazidime, CAZ (30 μg/ml); ceftriaxone, CRO (30 μg/ml); ciprofloxacin, CIP (5 μg/ml); colistin, CST (10 μg/ml); doxycycline, DOX (30 μg/ml); enrofloxacin, ELX (10 μg/ml); ertapenem, ETP (10 μg/ml); gentamicin, GEN (10 μg/ml); imipenem, IPM (10 μg/ml); levofloxacin, LVX (5 μg/ml); norfloxacin, NOR (10 μg/ml); novobiocin, NOV (30 μg/ml); piperacillin, PIP (100 μg/ml); polymyxin B, PMB (300 μg/ml); spectinomycin, SPT (100 μg/ml); streptomycin, STR (10 μg/ml); tetracycline, TET (30 μg/ml); ticarcillin, TIC (75 μg/ml); tigecycline, TGC (15 μg/ml); tobramycin, TOB (10 μg/ml); trimethoprim, TMP (5 μg/ml). The data for representative drugs are shown here. (B) Sensitivities of WT, ΔkpnEF, and ΔkpnEFΩkpnEF strains to different concentrations of SDS. The survival ability of the WT strain in SDS at 1,024 μg/ml was ∼1.22-fold greater, in SDS at 2,048 μg/ml it was ∼1.3-fold greater, in SDS at 4,096 μg/ml it was ∼1.15-fold greater, in SDS at 8,192 μg/ml it was ∼1.64-fold greater, and in SDS at 16,834 μg/ml it was 4-fold greater compared to the ΔkpnEF strain. (C) Susceptibilities of WT, ΔkpnEF, and ΔkpnEFΩkpnEF strains to different concentrations of deoxycholate. The survival ability of the WT strain in deoxycholate at 128 μg/ml was ∼1.13-fold greater, in deoxycholate at 256 μg/ml it was ∼1.2-fold greater, in deoxycholate at 512 μg/ml it was ∼1.26-fold greater, in deoxycholate at 1,024 μg/ml it was ∼1.25-fold greater, and in deoxycholate at 2,048 μg/ml it was 1.71-fold greater compared to the ΔkpnEF strain. (D) Sensitivities of WT, ΔkpnEF, and ΔkpnEFΩkpnEF strains to different concentrations of EtBr. The survival ability of the WT strain in EtBr at 8 μg/ml was ∼1.18-fold greater, in EtBr at 64 μg/ml it was ∼1.29-fold greater, in EtBr at 128 μg/ml it was ∼1.44-fold greater, in EtBr at 256 μg/ml it was ∼1.94-fold greater, and in EtBr at 512 μg/ml it was 3.57-fold greater compared to the ΔkpnEF strain. (E) Susceptibilities of WT, ΔkpnEF, and ΔkpnEFΩkpnEF strains to different concentrations of acriflavine. The survival ability of the WT strain in EtBr at 8 μg/ml was ∼1.58-fold greater, in EtBr at 64 μg/ml it was ∼1.57-fold greater, and in EtBr at 128 μg/ml it was ∼3-fold greater compared to the ΔkpnEF strain. The percent survival was calculated by comparison of the viable cells in the WT. The data are means of measurements made in triplicate and performed three times. *, Significant difference (P < 0.05, Student t test).
