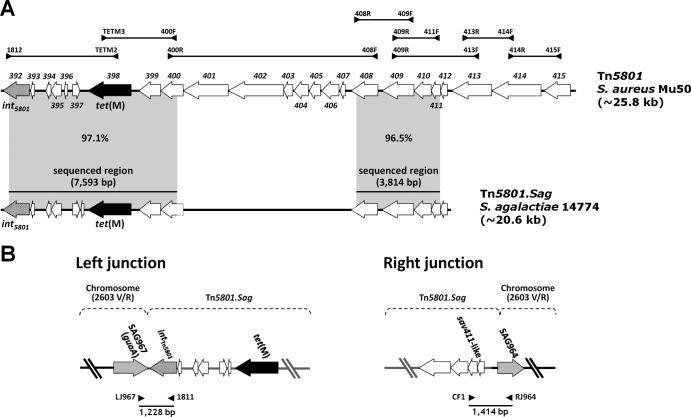
Fig 1.
Schematic representation of Tn5801.Sag from S. agalactiae strain 14774 (A) and its chromosomal integration (left and right junctions) (B). (A) Tn5801.Sag was determined by PCR mapping and sequencing of two regions. The primers used are listed in Table 1. The mapping strategy is outlined in the upper portion (the amplicons used to detect individual ORFs, i.e., obtained by pairing two primers internal to the same ORF, are not shown). The two regions sequenced initially (7,593 bp, left, and 3,814 bp, right) are indicated by horizontal bars. Tn5801.Sag is compared to Tn5801 from S. aureus Mu50, where ORFs are numbered sav392 to sav415 according to the original designations (DDBJ accession no. BA000017); percent DNA identities are reported in gray areas between sequenced regions. tet(M) and int5801 are represented as black and spotted arrows, respectively. (B) Tn5801.Sag was integrated at the 3′ end of the guaA gene. This gene, detected in all S. agalactiae genomes sequenced to date, corresponds to ORF967 from S. agalactiae 2603V/R (GenBank accession no. AE009948), from which chromosomal ORF designations derive. The amplicons obtained by pairing primers LJ967/1811 (left junction) and CF1/RJ964 (right junction), whose sequencing extended the two portions of Tn5801.Sag sequenced initially, are shown as bars. tet(M) and int5801 are represented as black and spotted arrows, respectively, and other Tn5801.Sag ORFs as white arrows; chromosomal ORFs are depicted as gray arrows.