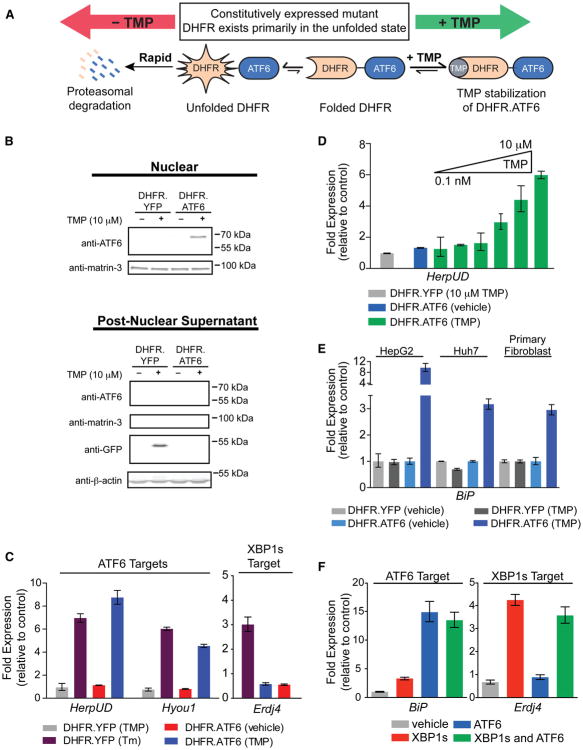
Figure 1. Orthogonal, Ligand-Dependent Control of XBP1s and ATF6 Transcriptional Activity.
(A) Model illustrating the TMP-mediated, posttranslational regulation of DHFR.ATF6.
(B) Immunoblot of nuclear (top) and postnuclear (bottom) fractions from HEK293T-REx cells expressing DHFR.YFP or DHFR.ATF6 treated 12 hr with TMP (10 μM). The immunoblot of matrin-3 shows the efficiency of the nuclear extraction.
(C) qPCR analysis of Hyou1, HerpUD, and Erdj4 in HEK293T-REx cells expressing DHFR.YFP or DHFR.ATF6 following a 12 hr treatment with TMP (10 μM) or a 6 hr treatment with Tm (10 μg/ml). qPCR data are reported relative to vehicle-treated cells expressing DHFR.YFP. qPCR data are reported as the mean ± 95% confidence interval.
(D) TMP dose dependence of HerpUD upregulation in HEK293T-REx cells expressing DHFR.ATF6 (12 hr treatments with TMP). qPCR data are reported as the mean ± 95% confidence interval.
(E) qPCR analysis of the ATF6 target gene BiP in HepG2, Huh7, or primary fibroblast cells transiently transduced with DHFR.YFP- or DHFR.ATF6-expressing adenoviruses and treated for 12 hr with 100 μM TMP or vehicle. qPCR data are reported relative to the corresponding vehicle-treated cells. qPCR data are reported as the mean ± 95% confidence interval.
(F) qPCR analysis of BiP and Erdj4 in HEK293DAX cells following a 12 hr activation of XBP1s (dox; 1 μg/ml), DHFR.ATF6 (TMP; 10 μM), or both. qPCR data are reported relative to vehicle-treated HEK293DYG cells. qPCR data are reported as the mean ± 95% confidence interval. See also Figure S1 and Table S4.