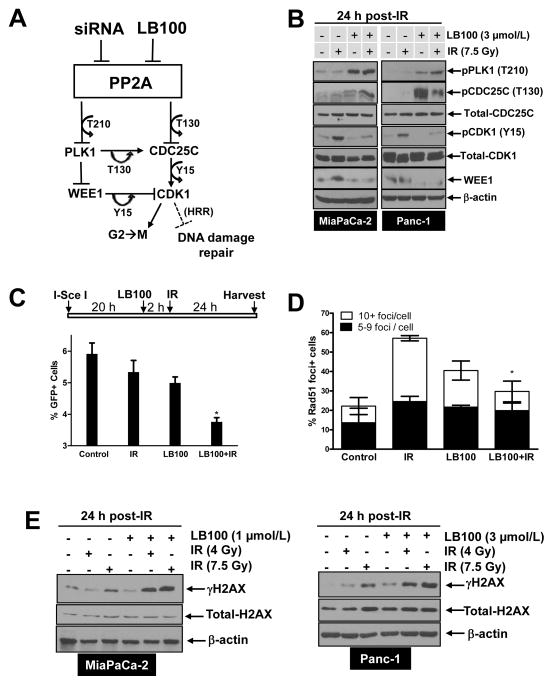
Figure 4. Mechanisms of LB100-mediated radiosensitization.
A, Schematic diagram illustrating the consequences of PP2A inhibition. Inhibition of PP2A by siRNA or LB100 results in activation of PLK1 and CDC25C (via accumulation of T210 and T130 phosphorylations, respectively). Active PLK1 positively regulates CDC25C (T130) and negatively regulates WEE1, resulting in enhanced dephosphorylation of CDK1 (Y15) by CDC25C and impaired phosphorylation of CDK1 (Y15) by WEE1, leading to activation of CDK1. Active CDK1, together with cyclin B is the key regulator of the G2/M cell cycle transition. In addition, CDK1 may negatively regulate HRR. B, E, MiaPaCa-2 and Panc-1 cells were treated with LB100 for 2 hours pre- and 24 hours post-IR. At the end of treatment, cells were harvested for immunoblot analysis. C, MiaPaCa-2-DR-GFP cells were treated as illustrated and the percentage of GFP positive cells was measured by flow cytometry. Data are expressed as the mean percentage of GFP positive cells ± SE from 3 independent experiments. Statistical significance versus IR* is indicated. D, MiaPaCa-2 cells were treated as described in Fig. 4B and fixed for immunofluorescence 6 hours post-IR. Data are the mean percentage of Rad51 positive nuclei ± SE (n = 3). Statistical significance versus IR* is indicated (C, D).