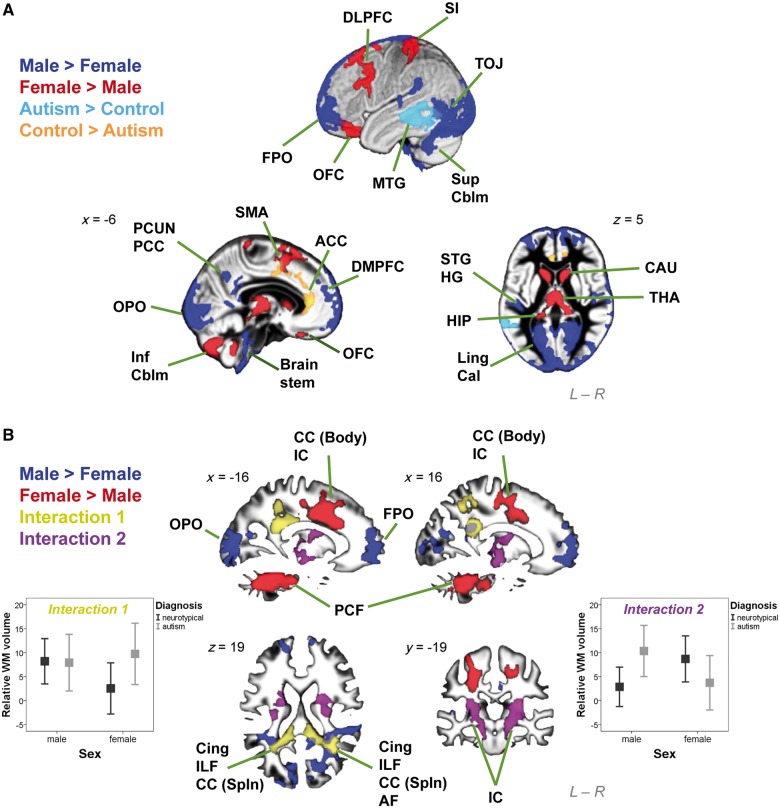
Figure 1.
Brain structures showing significant interaction and main effects in the 2 x 2 factorial design VBM. (A) Clusters were overlaid on the grey matter segment of the study-specific template. Substantially large clusters where males are larger than females are in dark blue, females larger than males in red, neurotypical controls larger than autism groups in orange, and autism groups larger than neurotypical controls in light blue. (B) Clusters were overlaid on the white matter segment of the study-specific template. Substantially large clusters where males are larger than females are in dark blue, and females larger than males in red. Importantly, large clusters with significant sex × diagnosis interactions were noted. A pattern of FA > FC but MA = MC (left error-bar graph; y-axis indicates relative white matter volume [arbitrary unit] and error bar indicates standard error of the mean) was identified in two clusters (yellow), and a pattern of MA > MC but FA < FC (right error-bar graph) in two clusters (purple). ACC = anterior cingulate cortex; AF = arcuate fasciculus; Cal = calcarine; CAU = caudate; CC (Body) = body of corpus callosum; CC (Spln) = splenium of corpus callosum; Cing = cingulum; DLPFC = dorsolateral prefrontal cortex; DMPFC = dorsomedial prefrontal cortex; FPO = frontal pole; HG = Heschl gyrus; HIP = hippocampus; IC = internal capsule; ILF = inferior longitudinal fasciculus; Inf Cblm = inferior cerebellum; Ling = lingual gyrus; MTG = middle temporal gyrus; OFC = orbitofrontal cortex; OPO = occipital pole; PCC = posterior cingulate cortex; PCF = ponto-cerebellar fibres; PCUN = precuneus; SI = primary somatosensory cortex; SMA = supplementary motor area; STG = superior temporal gyrus; Sup Cblm = superior cerebellum; THA = thalamus; TOJ = temporo-occipital junction.