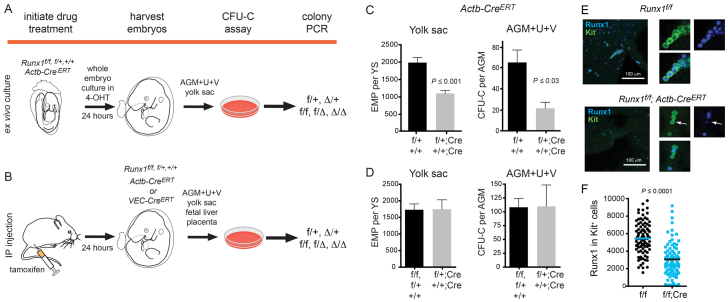
Fig. 1.
Experimental strategy for deleting Runx1. (A) Runx1 was deleted by culturing whole embryos ex vivo for 24 hours with 4-OHT. Embryos were staged prior to and at the end of the culture period. Hematopoietic tissues were washed, dissociated and plated in colony assays. Multiple individual colonies were analyzed by PCR for deletion of Runx1f alleles. f/+ and Δ/+ represent colonies from a Runx1f/+; CreERT conceptus in which the Runx1f allele was not deleted, or was deleted, respectively. f/f, f/Δ and Δ/Δ represent colonies from Runx1f/f; CreERT conceptuses in which no, one, or both Runx1f alleles were deleted, respectively. (B) All deletions initiated at E9.5 onwards were performed by injecting pregnant dams with tamoxifen. Hematopoiesis was analyzed as shown in A. (C) The impact of Cre activation on progenitors following exposure to 4-OHT ex vivo in whole embryo cultures. Deletion was performed between E8.5 and E9.5. Genotypes of conceptuses are Runx1f/+ (f/+) and Runx1+/+ (+/+) (n=21), or Runx1f/+; Actb-CreERT (f/+; Cre) and Runx1+/+; Actb-CreERT (+/+; Cre) (n=8). (D) Progenitor numbers following tamoxifen injection of pregnant dams. Deletions were performed at E9.5 and embryos harvested at E10.5. All deletions were carried out with Actb-CreERT. +/+, f/+ and f/f, n=10 in yolk sac and n=8 in AGM+U+V. +/+; Cre and f/+; Cre, n=5 in yolk sac and n=6 in AGM+U+V. In C and D, error bars indicate s.e.m. (E) Whole-mount immunofluorescence of E10.5 yolk sacs harvested from dams injected with tamoxifen at E9.5, using antibodies recognizing endogenous Runx1 and Kit (maximum of 20 3-μm z-sections). Panels on the right are examples of Kit+ cells (green) with Runx1+ nuclei (blue). Arrows indicate a Kit+ cell with low Runx1 nuclear staining. Nuclear fluorescence intensity of Runx1 in individual Kit+ cells was quantified and plotted in panel F. (F) The average corrected nuclear fluorescence of Runx1 in 100 Kit+ cells.