Fig. 1.
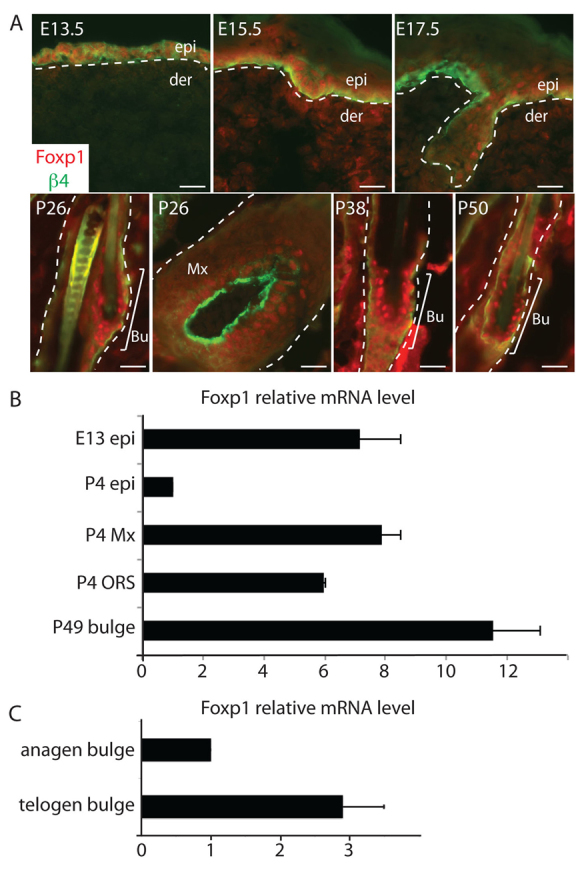
Foxp1 marks embryonic epidermal cells, adult hair follicle stem cells and transit amplifying cells in skin. (A) Immunofluorescence images of skins at different stages of development. Skins of the indicated stage of development were embedded in OCT, sectioned, and immunostained with antibodies against Foxp1 (red) and integrin β4 (green), which marks the basement membrane. White dashed lines denote epidermal-dermal border. Scale bars: 50 μm. (B) Real-time PCR analysis of Foxp1 expression in different compartments of the epidermis at different stages of development. Real-time PCR analysis was performed on cDNA synthesized from mRNA that was isolated from specified epidermal compartments at the indicated time of development. (C) Real-time PCR analysis of Foxp1 expression in anagen and telogen bulge HFSCs. Real-time PCR analysis was performed on cDNA synthesized from total RNA that was isolated from FACS-sorted anagen (P28) and telogen (P49) bulge HFSCs. Error bars represent s.d. Bu, bulge; der, dermis; epi, epidermis; Mx, matrix; ORS, outer root sheath.
