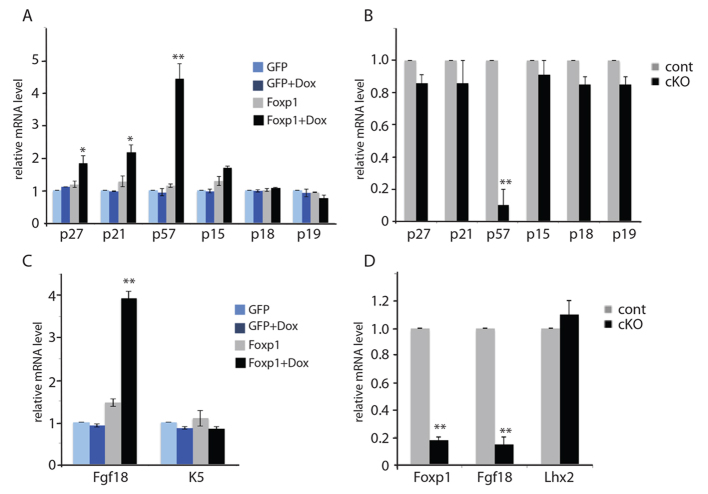
Fig. 6.
Foxp1 controls the expression of p57KIP2 and Fgf18. (A) Real-time PCR analysis shows that overexpression of Foxp1 results in the induction of the CDK inhibitor p57KIP2. Keratinocytes were transduced to express tet-inducible HA-tagged Foxp1 or GFP and were selected by drug selection. Real-time PCR was performed on cDNA synthesized from mRNA that was isolated from the transduced cells that were grown in media with doxycycline (Dox) or vehicle for 24 hours. (B) Real-time PCR analysis shows that loss of Foxp1 results in reduction of p57KIP2 expression. Real-time PCR was performed on cDNA synthesized from RNA that was isolated from HFSCs of Foxp1 cKO or control skins. (C) Real-time PCR analysis shows that overexpression of Foxp1 results in the induction of Fgf18 mRNA expression. Keratinocytes were transduced to express tet-inducible HA-tagged Foxp1 or GFP and were selected with G418. Real-time PCR was performed on cDNA synthesized from RNA that were isolated from the transduced cells that were grown in media with Dox or vehicle for 24 hours. (D) Real-time PCR analysis shows that loss of Foxp1 results in reduction of Fgf18 mRNA expression. Real-time PCR was performed on cDNA synthesized from RNA that was isolated from HFSCs of Foxp1 cKO or control skins. Data are mean ± s.e.m. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. p27, Cdkn1b; p21, Cdkn1a; p57, Cdkn1c; p15, Cdkn2b; p18, Cdkn2c; p19, Cdkn2d.