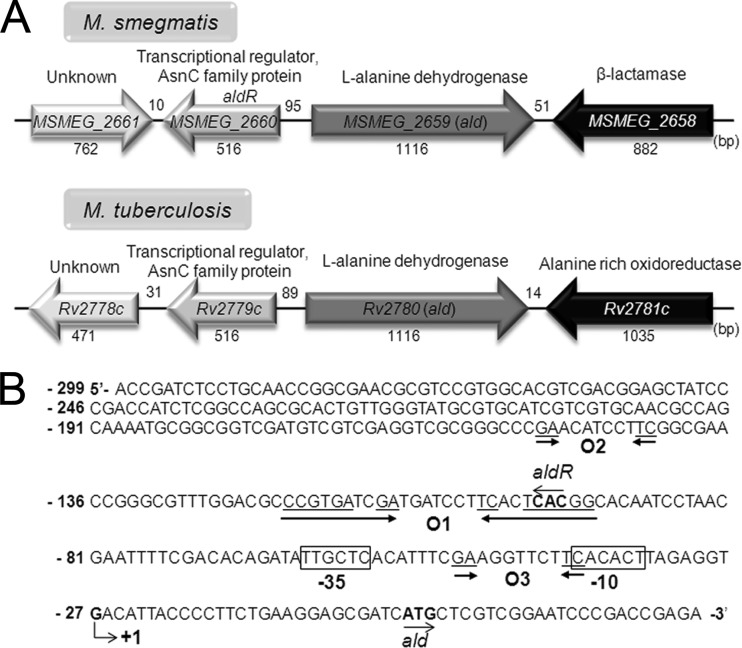
Fig 3.
Genetic organization of the ald locus and the putative cis-acting elements for ald expression. (A) The ald genes and their flanking genes in M. smegmatis mc2155 and M. tuberculosis H37Rv. The genes of the putative transcriptional regulators, MSMEG_2660 (aldR) and Rv2779c, are divergently located upstream of the ald genes. The lengths of genes and intergenic regions are given as the nucleotide numbers below and above their names, respectively. (B) The transcription start site (+1) of the ald gene of M. smegmatis was previously reported to be a guanosine residue that is located 27 nucleotides upstream of the start codon of ald (2). The −10 and −35 regions of the putative promoter for ald deduced from the transcription start point are boxed. The putative AldR binding site (O1), which shows an interrupted inverted repeat sequence ( CCGTGAN2GA-N7-TCN2TCACGG ), is marked by two head-facing arrows. The O2 and O3 sequences (GA-N7-TC) exhibiting partial sequence similarity to O1 are indicated by two arrows. The start codons of ald and aldR are highlighted in boldface and by the arrows indicating the transcriptional direction. The numbers on the left of the nucleotide sequence indicate the positions of the leftmost nucleotides relative to the ald gene.