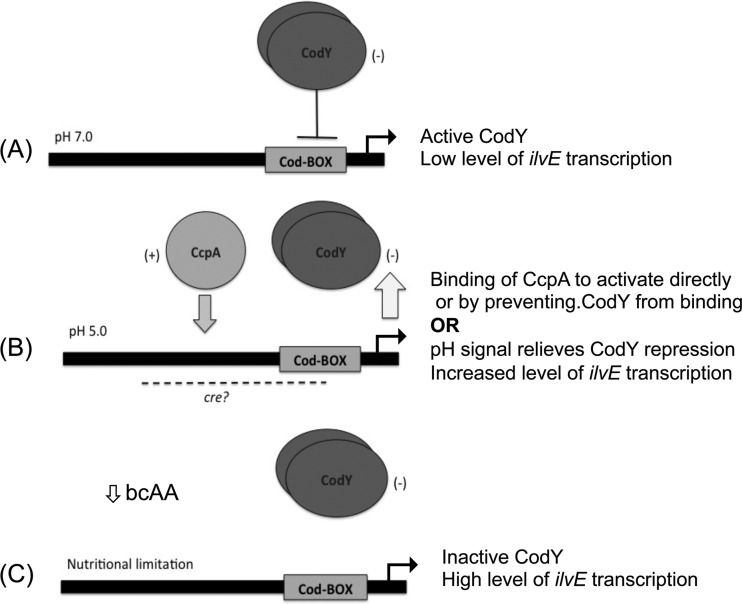
Fig 10.
Proposed model for coordinated regulation of ilvE by CcpA and CodY. (A) The regulation of ilvE in S. mutans combines multiple signals, depending on the growth conditions and extracellular environment. Under nonacidic, nutrient-rich environmental conditions (pH 7.0), ilvE transcription is repressed by the action of CodY. (B) Under acidic conditions (pH 5.0), resulting from the metabolism of carbohydrates and subsequent depletion of nutrients, CodY derepression in combination with CcpA activation allows for increased transcription of ilvE. The CodY and CcpA proteins regulate ilvE by binding to domains within the ilvE intergenic region. The CodY-binding domain is required for interaction. The CcpA-binding domain has yet to be determined. (C) Nutritional regulation is solely dependent on CodY. CodY senses the levels of intracellular amino acids, which drop under nutrient-limiting conditions. Binding of CodY to its target genes is enhanced in the presence of isoleucine; hence, as the levels of bcAAs decrease, CodY repression is alleviated.