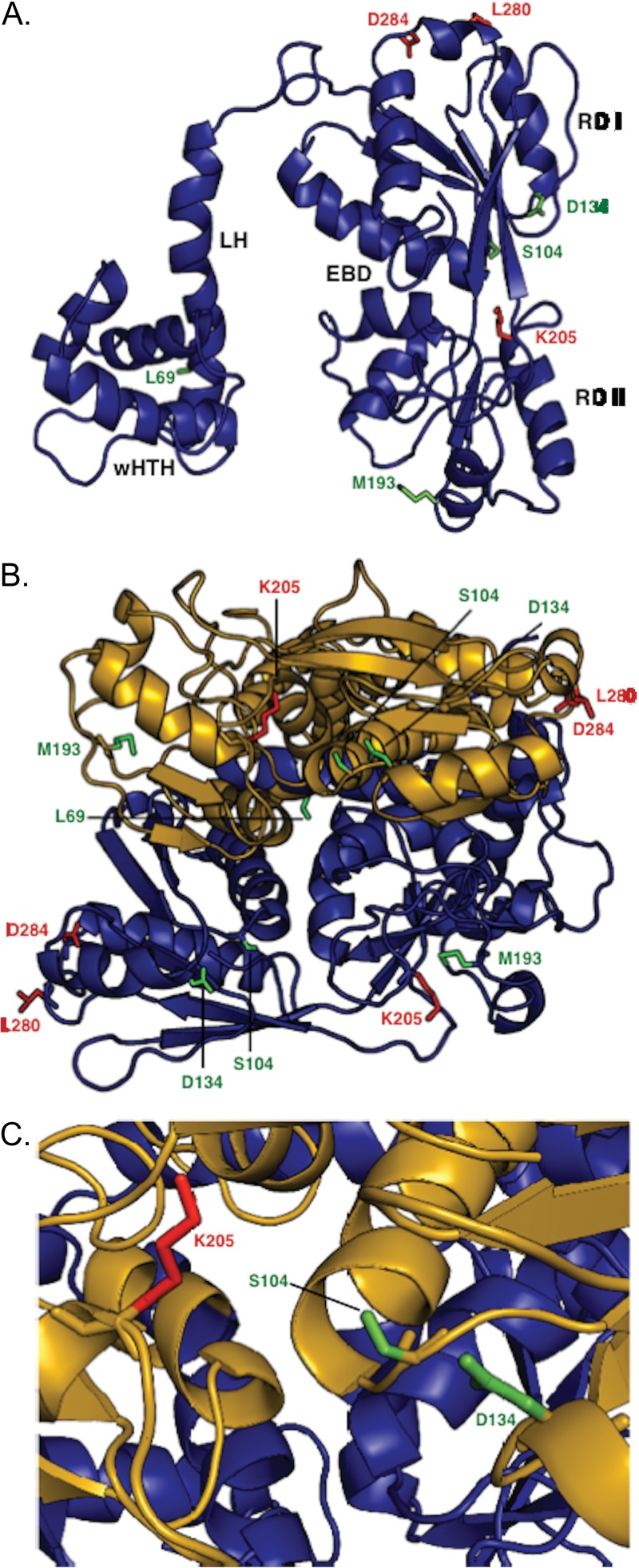
Fig 5.
Structural model of NodD1 based on crystal structures of Burkholderia sp. DntR (1UTB) (40), Acinetobacter baylyi BenM (3K1N) (41), Ralstonia eutropha CbnR (1IZ1) (42), Neisseria meningitidis CrgA (3HHG) (43), and N. meningitidis OxyR (3JV9) (44). All structures shown in backbone ribbon denote α-helices and β-sheets. Mutant residues are shown in stick figure. Residues L69, S104, D134, and M193, representing type I NodD1 mutants, are shown in green. Residues K205, L280F, and D284, representing type II to IV NodD1 mutants, are shown in red. (A) The modeled NodD1 monomer is shown with the various domains labeled: wHTH, winged helix-turn-helix; LH, linker helix; RD I, regulatory domain I; RD II, regulatory domain II; EBD, effector binding domain. (B) Model of NodD1 as a dimer. The EBDs are formed by clefts in each monomer. (C) Closeup view of the modeled NodD1 EBD.