Fig 1.
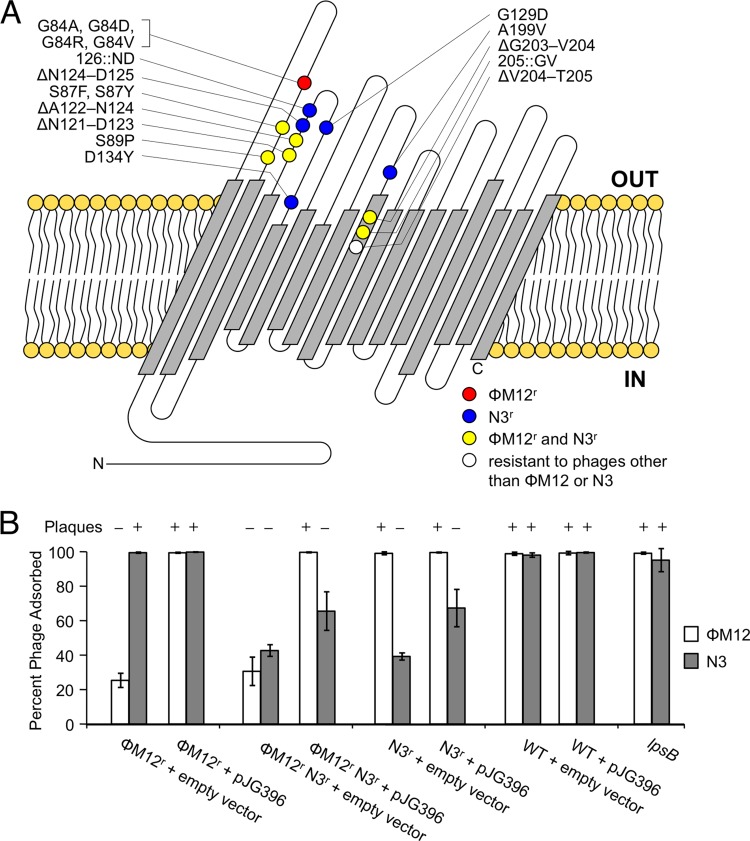
RopA1 is the site of phage adsorption for ΦM12 and N3. (A) Predicted RopA1 outer membrane topology, along with alterations that give resistance to ΦM12 (red), N3 (blue), both (yellow), or other S. meliloti phages (white), is shown. (B) A ΦM12-resistant (ΦM12r) mutant (ropA1G84A), a ΦM12r N3r mutant (ropA1ΔG203-V204), and an N3r mutant (ropA1ΔN124-D125) were tested for phage adsorption (n = 3). Strains harbored either the empty vector control plasmid (pRF771) or the wild-type ropA1 clone pJG396. Error bars represent the standard deviations (SD). The susceptibility of these strains to plaque formation is also indicated.