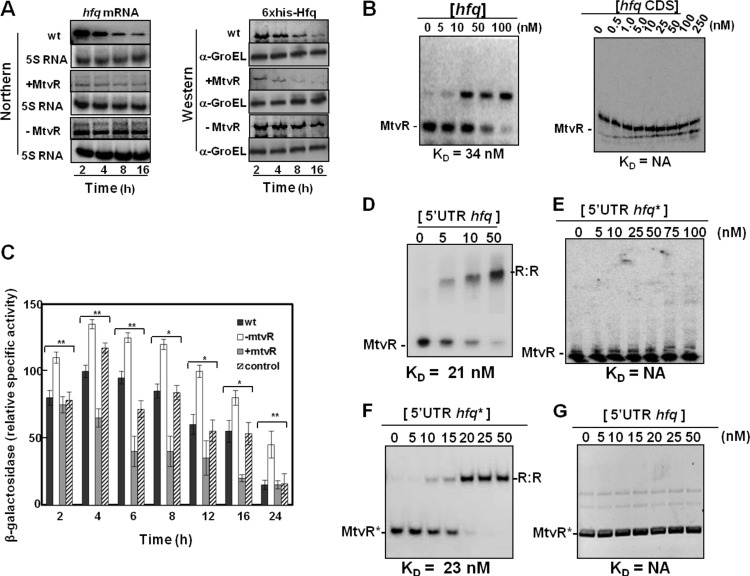
Fig 2.
MtvR regulates hfq expression through interaction with its 5′ leader region. (A) Ability of MtvR to affect hfq mRNA and protein levels as evaluated by Northern and Western blotting, respectively, in the wt and derivative strains overexpressing MtvR or with the sRNA silenced. (B) EMSAs using 25 nM MtvR and the indicated concentrations of the hfq full mRNA (left) or the hfq coding region (CDS) (right). KD values are shown below each panel. (C) β-Galactosidase activity of the hfq 5′ UTR-LacZ fusion. (D to G) The translational regulation of the LacZ protein was determined in the wt and derivatives with MtvR silenced (−MtvR) or overexpressing MtvR (+MtvR) transformed with pCGR33. EMSAs using 25 nM MtvR together with the indicated concentrations of the hfq 5′ UTR (5′ UTR hfq) (D) or the mutated hfq 5′ UTR (5′ UTR hfq*) (E), or using 25 nM mutated MtvR (MtvR*) with the indicated concentrations of the mutated hfq 5′ UTR (5′ UTR hfq*) (F) or with the native 5′ UTR of hfq (5′ UTR hfq) (G). NA, not applicable. The error bars indicate standard deviations (SD). Asterisks represent mutated forms of the RNAs.