Fig 7.
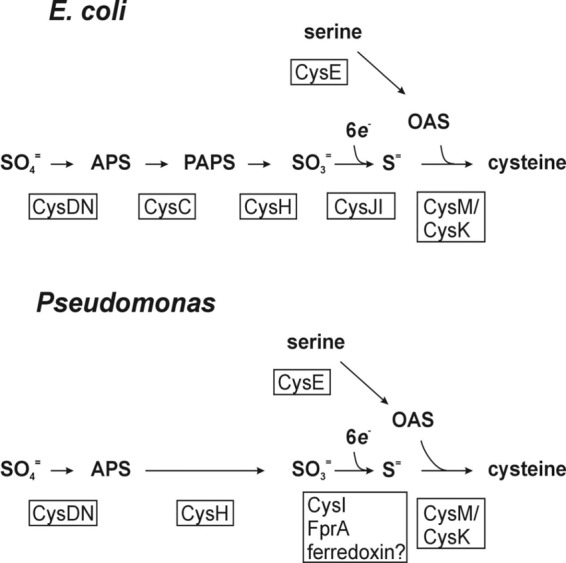
Pathway of sulfate assimilation/cysteine biosynthesis in enterics versus pseudomonads. Intermediates of cysteine biosynthesis are shown in bold. Gene products with relevant enzymatic activities (CysDN, CysC, etc.) are given below or beside the respective steps in boxes. Abbreviations: APS, adenosine phosphosulfate; PAPS, phosphoadenosine phosphosulfate; OAS, O-acetylserine. The negative allosteric regulation of CysE activity by intracellular cysteine, and the requirement for N-acetylserine (a product of spontaneous rearrangement of OAS) to induce sulfate assimilatory gene expression (via CysB), affords coordination between serine activation and sulfate activation/reduction activities in response to metabolic demand for cysteine (46).
